Conny Waters – AncientPages.com – The distant ancestors of modern horses had hooved toes instead of a single hoof, which vanished over time, according to researchers.
The animals, such as the Eocene Hyracotherium, had feet like those of a modern tapir: four toes in front and three behind, each individually hooved with an underlying foot pad.
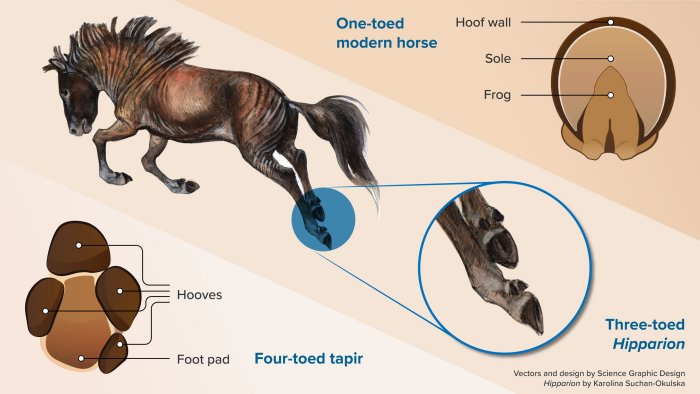
Plantar (underneath) view of feet of a four-toed tapir (left) and a one-toed horse (right) by Nuria Melisa Morales-García. In the middle, a reconstruction of the extinct three-toed horse Hipparion, by Karolina Suchan-Okulska. Overall design by Morales-García.
In contrast, modern equids such as horses, ᴀsses, and zebras, have only a single toe, the left over original third toe on each foot, encased in a thick-walled keratinous hoof, with an underlying triangular frog on the sole that acts as a shock absorber.
An international team of scientists, from the UK, the US, and the Netherlands, analysed hoof prints and foot bones from modern horses and fossil records to discover what happened to the lost digits.
Author Professor Christine Janis from the University of Bristol’s School of Earth Sciences explained: “The upper portions – the remains of the additional hand and foot bones – remain as ‘splint bones’ fused with the remaining central one, but where are the fingers and toes?”
“In later fossil horses there were only three toes front and back. The extra toes, known as side toes, in these horses were smaller and shorter than in a tapir, and likely did not touch the ground under normal circumstances, but they may have provided support in exceptional situations, such as sliding or forceful impact.”
In findings, published today in Royal Society Open Science, they confirm the older notion that these toes really have been completely lost in evolution, not somehow retained within the hoof, as proposed in another recent paper published in the same journal in 2018.
Lead author Professor Alan Vincelette, of St. John’s Seminary, Camarillo, California pointed out: “Although it does seem that remainders of the proximal (upper portions) of the side digits have been retained in modern horses, as the earlier 2018 paper claimed, the distal (lower portions, or toes) have simply been lost.
The 2018 paper proposed that in modern horses these side toes are retained within the hoof of the central toe, in part contributing to the frog – although there are no actual bones within the frog.
This was partially based on an interpretation of the hoof prints of an extinct three-toed horse, Hipparion (not on the direct line to modern horses) from Laetoli in Tanzania 3.7 million years ago, the same site that yielded the famous foot prints of the hominid Australopithecus. These hoof prints apparently lacked a frog, and this added weight to the notion that the side toes of horses like Hipparion now contribute to the frog of modern horses.
While not all hoof prints of modern horses with frogs record its presence, an undoubted frog can be seen in many hoof prints that are known to have been made by three-toed horses. These observations cast doubt on the notion that the frog of modern horse hooves formed out of the side toes of tridactyl equids.
“While the notion that modern horses have retained all of their original toes as within-hoof remnants is a novel one, and so rather appealing, it can be shown to be incorrect,”author Professor Christine Janis from the University of Bristol’s School of Earth Sciences, said in a press release.
Professor Vincelette added: “The frog of the horse’s hoof evolved independently of the side toes as a unique structure providing shock absorption and traction during locomotion.”
The team also show that the feet of one-toed horses have a different shape from the main toe of the foot of three-toed horses, being round rather than oval, a difference that may be related to differences in weight distribution and/or ecological habitat.
Paper
Written by Conny Waters – AncientPages.com Staff Writer





