Jan Bartek – AncientPages.com – One of the most fascinating sites where scientists can study the history of Neolithic people is the Galería del Sílex Cave, part of Spain’s Sierra de Atapuerca cave system.
At the end of the Bronze Age, the cave entrance was sealed by our ancestors, and the place was turned into an intact time capsule until its discovery in 1972. Based on archaeological discoveries, it is known people lived in the Galería del Sílex Cave for thousands of years.
Geographic distribution of Early Neolithic sites (before 4,800 cal BCE) in the Iberian Peninsula . Credit: Quaternary Science Reviews (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2023.108256
As part of a new study conducted by the Universidad de Alcala, Spain, scientists have re-examined ancient human remains found in the cave, and the science team presents intriguing discoveries shedding light on the funerary practices of early Neolithic people. Scientists have also found evidence of different uses of caves during the Holocene in the Atapuerca sites.
In the study, published in Quaternary Science Reviews, the team discusses the analysis of the site, fossils shedding new light on the individuals who once, a long time ago, lived in the cave.
Inside the Galería del Sílex Cave, scientists have found 53 panels of engravings and red and black cave paintings. Thousands of human and animal remains, dozens of fire hearth remnants, fragments of ceramic vessels, and faunal remains have also been unearthed at the site. Who were these people, and what was their story? Why does the case contain so many bones?
Radiocarbon conducted on bone samples from three bone samples belonging to different individuals revealed the oldest person lived in the cave about 6,250 years ago.
The human fossils in Galería del Sílex are attributed to the Neolithic period and correspond “to a minimum number of three individuals that have been radiocarbon dated to the last third of the 6th-millennium cal BCE. Thus, the fossils from Galería del Sílex are among the oldest Neolithic human remains in the interior of the Iberian Peninsula,” the research team writes in the study.

Credit: Adobe Stock – Matyas Rehak
Scientists suggest the cave was used for burials and funerary rituals because the remains were found within two pits (simas) located more than three hundred meters from the ancient entrance rather than in a domestic context within the cave.
“Among the human remains, two sets stand out because they were isolated and deposited at the foot of two pits (called Sima A and Sima B), located more than 300 m from the entrance.
This suggests that Galería del Sílex could have been an area reserved for depositing deceased humans during the Early Neolithic. Given the scarcity of this kind of funerary cave in the Spanish northern plateau during the Early Neolithic, the data from the Galería del Sílex add to our knowledge of human mortuary behavior during this period,” the study informs.
In the pit, Sima B, the research team found bones belonging to three humans. One of them had all skeletal remains accounted for, indicating the individual was placed in the pit directly after death.
Scientists could confirm human remains in Sima B were found grouped together on a ledge at the upper part of the shaft and deliberately placed there. Unfortunately, there is no pH๏τographic documentation of their position.
From Sima A, scientists recovered the Early Neolithic remains of two people and six ceramic vessels placed in the pit as burial offerings.
The discovery of funeral pits in the Spanish cave is of great historical significance as it provides data on early Neolithic funerary practices in Iberia.
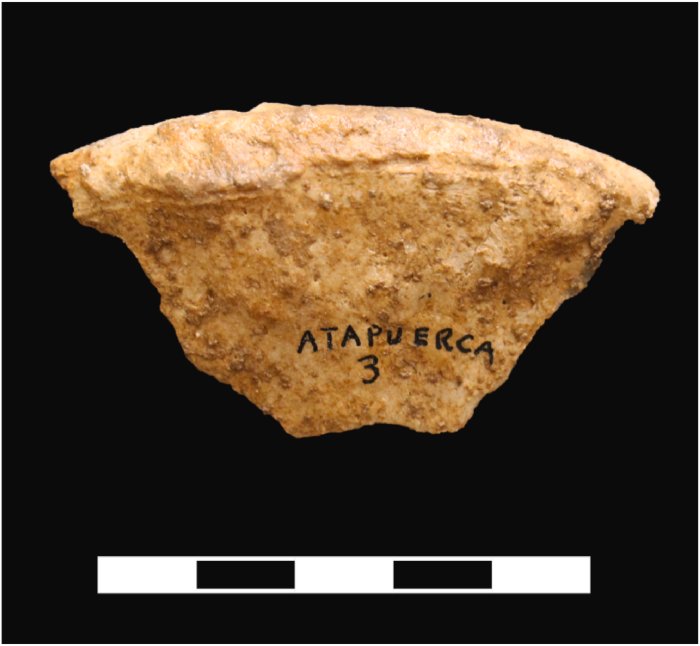

Iliac fragment (CMS-1001.40) attributed to Individual 1. Iliac crest completely fused is shown. Scale bar = 5 cm. Credit: Quaternary Science Reviews (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2023.108256
Early Neolithic remains in the area are “not abundant,” according to the study, and hardly ever found in this context. “The low population density of the first Neolithic settlers, in addition to their continuously changing settlements, could explain the lack of visibility of death from that period,” the study informs.
See also: More Archaeology News
Another intriguing archaeological finding concerns the representation of both Sєxes.
“With respect to the age at death and Sєx attributed to Early Neolithic individuals found in GS, it is noteworthy that both Sєxes are represented: there is one adult female individual and one adult male. This is remarkable because out of all Early Neolithic individuals from the Iberian Peninsula and the south of France, just 16% are women. The presence of a juvenile individual, female, in the GS sample is noteworthy as well, since Early Neolithic juveniles are also rarely represented on the Iberian Peninsula and in the south of France, making up just 21% of the total,” the science team writes in the study.
The study was published in the journal Quaternary Science Reviews
Written by Jan Bartek – AncientPages.com Staff Writer





