Conny Waters – AncientPages.com – A perfectly preserved turtle fossil from Lower Bavaria yields important clues about both the species and the habitat that existed in southern Germany 150 million years ago.

Image credit: University of Tübingen
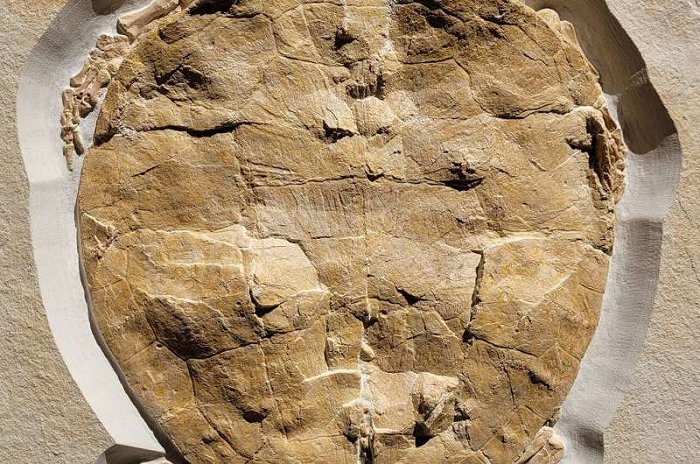
The fossil is the best-preserved specimen of Solnhofia parsonsi found to date. Its forelimbs and hind limbs are comparatively short, suggesting that the turtle lived near the coast.
This in contrast with today’s sea turtles, which have elongated flippers and live in the open sea.
“No Solnhofia individual with such completely preserved extremities has ever been described before,” says Felix Augustin of the Biogeology working group at the University of Tübingen. The head and carapace of Solnhofia parsonsi are also clearly preserved.
Solnhofia parsonsi, DMA-JP-2004/005, from the Upper Jurᴀssic (Kimmeridgian) Torleite Formation of Painten. Credit: PLOS ONE (2023). DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0287936
The beak is long and pointed, the head is triangular, and at just over nine centimeters long, measures almost half the length of the carapace.
“Solnhofia may have used its large head to crush hard food items such as shelled invertebrates, as we see in some modern turtles, but it does not mean these were exclusively forming its diet,” Márton Rabi of the University of Tübingen and co-author of the study, which has now published in the journal PLOS ONE, said in a press release.
The name Solnhofia refers to the limestone deposits of Solnhofen—a place located south of Nuremberg in the valley of the Altmühl.
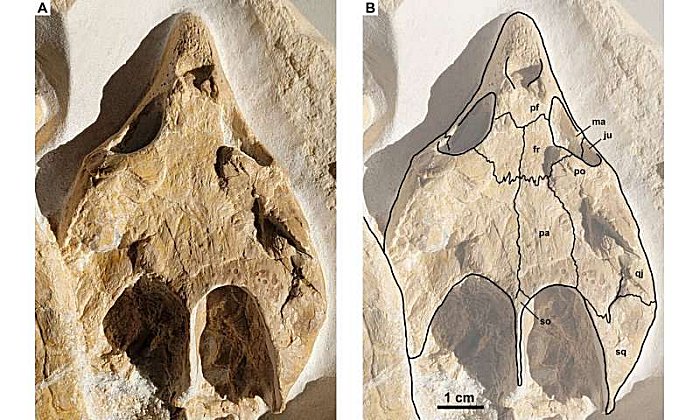
Solnhofia parsonsi, DMA-JP-2004/005, from the Upper Jurᴀssic (Kimmeridgian) Torleite Formation of Painten. Detail pH๏τograph (A) and drawing (B) of the skull. Both to the same scale. Abbreviations: fr, frontal; ju, jugal; ma, maxilla; pa, parietal; pf, prefrontal; po, posto
Famous fossils of one of the earliest birds, Archaeopteryx, and of many pterosaurs and marine reptiles have been found there.
The layers of the Solnhofen limestone, which are rich in fossils, run along the entire valley of the Altmühl. The fossil of Solnhofia parsonsi was found in a quarry in the Painten district west of Regensburg, where systematic digging for fossils has only been going on for about 20 years.
“The very good preservation of the fossils in the layers of limestone can be explained by the environmental conditions at the time,” says Andreas Matzke of the University of Tübingen and a co-author of the study.

Solnhofia parsonsi, DMA-JP-2004/005, from the Upper Jurᴀssic (Kimmeridgian) Torleite Formation of Painten. Detail pH๏τograph of the skull in left anterolateral (A) and right lateral view (B). Credit: PLOS ONE (2023). DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0287936
About 150 million years ago, a shallow, tropical sea stretched across southern Germany; it contained many islands and reefs that separated basins from the open sea. Floating particles sank to the basin floors, forming layers of limestone.
If an animal died, its remains also sank to the bottom. Due to the low exchange of the lagoon water with the open sea, the oxygen content there was so low and the salt content so high that ᴅᴇᴀᴅ plants and animals did not decompose. Plant and animal remains were preserved and fossilized in the limestone—often in unique detail.
The region is considered one of the world’s most important sites for fossils from the Mesozoic, which began about 250 million years ago and lasted until the extinction of the dinosaurs 66 million years ago.
The Solnhofia parsonsi fossil underscores the importance of the relatively recently discovered site in the Painten district.
The vertebrate fossils found in the limestone there are now being studied scientifically. The Dinosaur Museum in nearby Denkendorf exhibits the finds, including Solnhofia parsonsi.
Original publication
Written by Conny Waters – AncientPages.com Staff Writer






