A. Sutherland – AncientPages.com – Temple of the Crossed Hands (Templo de Las Manos Cruzadas) in Kotosh, Peru, is considered one of the oldest temples in Peru and America and dates back 4000 years.
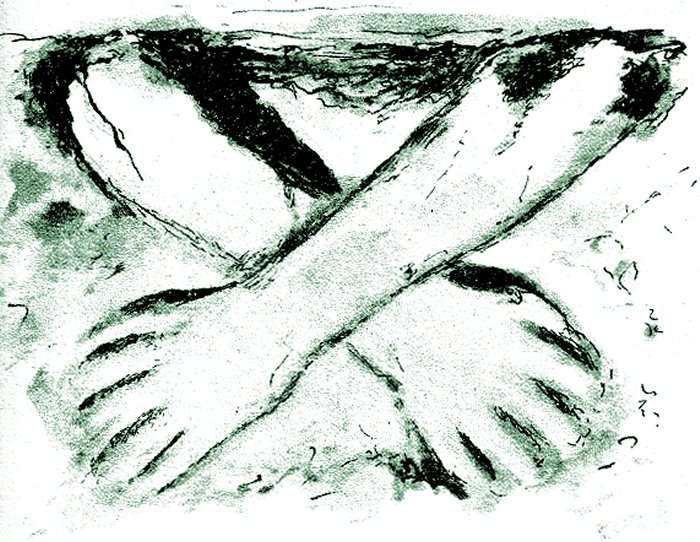

Terracota “Crossed arms” from Kotosh, 1800 BC. Image credit:
Kotosh represents a primary pre-Columbian ceremonial site located in the north-central highlands of Peru.
The first evidence of mᴀssive stone constructions from about 2000 BC suggests that complicated building work began centuries before anywhere else on the American continent.
The culture of Kotosh Waira-Jirca (1800-1300 BC) was concentrated in the Huánuco River basin, only 6km from Huánuco along the La Unión road.
More or less permanent settlement at the Kotosh ancient site predates the Chavín era by more than a thousand years, then it continued throughout the Inca occupation, right up to the Conquest.
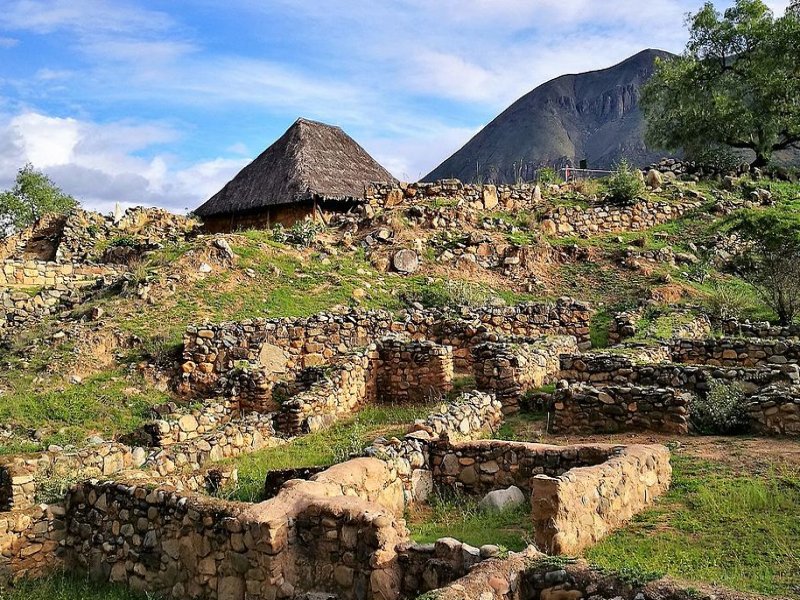

White Temple of Kotosh with the building of the Temple of the Hands. Image credit: – CC BY-SA 4.0
Today, the more than four-thousand-year-old Temple of the Crossed Hands lies in ruins and is poorly maintained.
The site was excavated by Japanese archaeologists sometime between 1958 and 1962. In 1960, the archaeologist Seichi Izumi discovered the first pair of crossed hands. Later, the second pair was found in 1963, supporting the construction theory of another temple under the crossed hands. Many interesting structures and some of the oldest known American sculptures followed the discovery.
The findings helped researchers shed more light on the technical and artistic complexity of the findings.
The most unique feature of the Kotosh complex is the crossed-hands symbol carved prominently in stone on the temple walls. Compiled by AncientPages.com
At the site are ruins of the White Temple with the Temple of the Hands. In a square is a huanca, a ritual object considered today a commemorative stone. The White Temple is so called because it had been plastered with white clay, making the structure appear painted white.
The Temple of the Crossed Hands is square-shaped, approximately 9.3 to 9.5 meters on a side, and has a central fire pit with a ventilation duct.
Achaeologists discovered skeletal remains of camelids and guinea pigs inside the temple’s niches, so it is believed that these niches were used for offerings. Ashes were found in the central fire pit, most probably used to burn the offerings.
Interestingly, other Kotosh objects also included bone stones, which is significant because identical pieces have been found in Caral.
Three cultural phases that preceded the Chavin culture (c. 900 – 200 BC) have been identified at the Kotosh site. However, some Kotosh elements have characteristics ᴀssociated with the Chavin culture. One of them is a tradition of decoration by using black paint on red ceramics. Kotosh’s people produced black polished incised pottery resembling classical Chavin pottery.
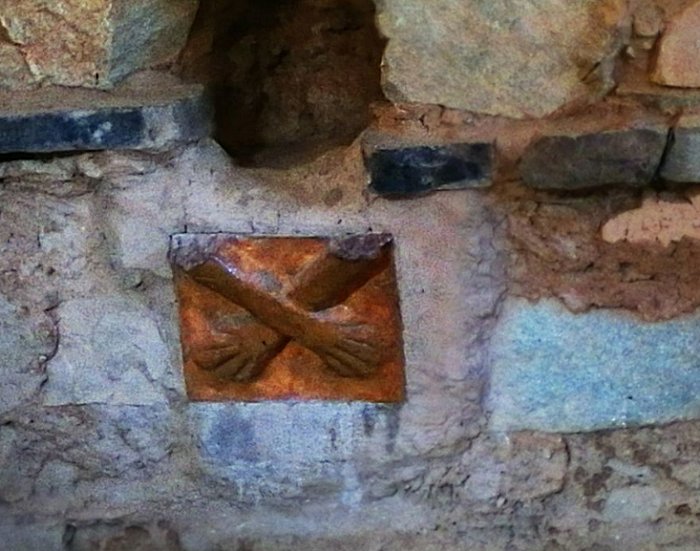

The Crossed Hands in the Temple of said name. Image credit: – CC BY-SA 4.0
This temple has a single entrance with a niche on each side facing inward. Below each slot, modeled in mud plaster, is a pair of crossed human forearms, some larger than the others, suggesting a male/female duality. The find may indicate the representation of the beginning of man and woman, symbolizing dualism.
Around the temple’s interior is a low stone bench; a firepit is in the center of the floor.
The unique feature of the Kotosh complex is the crossed-hands symbol carved prominently in stone on the temple walls and related to a very early culture about which archaeologists, unfortunately, know not much.
The ‘crossed human forearms’ symbol also decorates Peru’s Nuevo Sol coin. The crossed-arm design is believed to be the earliest example of “duality,” a central theme represented in Andean Ideology through the time of the Incas.
One set of arms has the left hand crossed over the right, while the other pair on the opposite wall has the right hand over the left. One pair of arms may represent the feminine because of their smaller size, while the second pair represents the masculine.
Currently, the Temple of the Crossed Hands contains two replicas made of fiberglᴀss.
Archeological excavations at the site of Kotosh revealed other even older structures in recent years. However, this particular complex still remains one of Peru’s most important archaeological sites.
Written by – A. Sutherland AncientPages.com Staff Writer
Updated on January 16, 2024
Copyright © AncientPages.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of AncientPages.com
Expand for references
References:
Kipfer Barbara Ann, Encyclopedic Dictionary of Archaeology
Huanuco.com
Marco Gamarra Galindo, The thousand-year-old Kotosh culture (La milenaria cultura Kotosh)





