Jan Bartek – AncientPages.com – A new analysis of the teeth remains found at the Lezetxiki site confirm that they belonged to Neanderthal individuals.
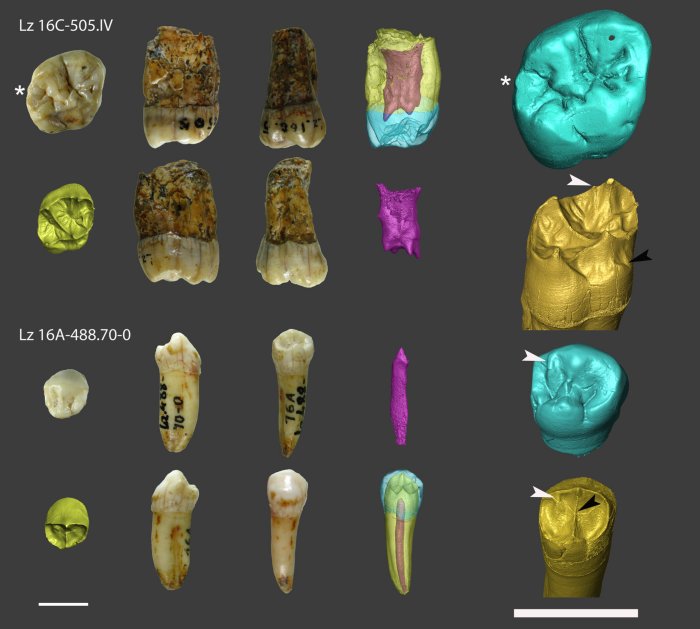
Dental remains from Lezetxiki. On the left, the teeth are shown in occlusal, mesial, lingual (top row), distal and buccal views (bottom row). The dentine model is shown in occlusal view, and the rendering of the whole teeth and tissues are in mesial view (M1) and buccal view (P3). The pulp chamber is in distal view. On the right side of the figure, the 3D models of enamel and dentine are shown at a larger scale for a detail description. The white arrow on the molar indicates the post-paracone tubercle, and the black arrow indicates the Carabelli’s tubercle. On the premolar, the white arrows indicate the Accesory distal crests in enamel and dentine, while the black arrow indicates the complete transverse crest. The scale bars represent 1 cm. Credit: American Journal of Biological Anthropology (2023). DOI: 10.1002/ajpa.24694
The Lezetxiki site (Arrasate, Gipuzkoa) is located in the midst of a karst complex with several partially dismantled cavities. Albeit it being discovered in 1927, almost thirty years pᴀssed before systematic excavations began. The site is considered to be one of the most important historically in terms of the prehistoric information it contains, particularly in the north of the Iberian Peninsula.
Practically all cultural phases of prehistory are represented in its stratigraphic sequence, with levels corresponding to the lower, middle and upper Paleolithic, and the site has yielded remains corresponding to different human groups.
This succession of occupations is highly important to researchers, particularly in the study of transition periods. This is the case of the site’s Level 3, in which the stone tools discovered correspond to a cultural period known as the Mousterian, i.e., to the cultural period corresponding to the Neanderthals.
But at the same time, this same level has yielded tools that are typical from the Aurignacian culture, i.e. a period corresponding to the Homo sapiens. This transitional period between the Mousterian and the Aurignacian is exactly one of the most important aspects of the site, given that it was the moment in which Neanderthals were being replaced by anatomically modern humans.
Radiocarbon dating of Level 3 made it possible for archaeologists to determine the chronological importance of the two sub-levels detected during the digs: one dating back 39,500 to 32,600 years ago from the Aurignacian culture and another from the Mousterian dating back minimum 46,500 years ago. Moreover, the stone sets recovered from this level were at first considered to be fully Mousterian, but in later studies classified them as Aurignacian.
This context of chronological and typological reᴀssignment of the material found at this level made it necessary to re-examine dental remains, given that the new information cast doubts on the taxonomic ᴀssignment of Neanderthals.
The teeth studied, an upper molar tooth and a lower premolar, from the excavations carried out by J. M. Barandiarán and discovered in 1966 were subject to a new paleoanthropological analysis, with the application of new techniques and methods, among them the dental tissue analysis from microcomputerized tomography scans and geometric morphometry.
The results obtained have been compared with other known specimens in the fossil record of the Middle Pleistocene, both Neanderthals, as well as modern humans from the Upper Paleolithic and modern humans from the Neolithic. The conclusion is clear, all the indicators obtained are consistent with a Neanderthal classification of the remains.
The dental remains from the Lezetxiki site therefore become the only ones belonging to adult Neanderthals from the region of the western Pyrenees recovered until now.
The reᴀssignment of the remains, together with the new data from the radiometric dating of the Lezetxiki levels, confirm a Neanderthal presence much later than previously thought in the north of the Iberian Peninsula in this transition period between the Middle and Upper Paleolithic.
The study, which included the involvement of the UAB and has been published in American Journal of Biological Anthropology, confirms a late presence of Neanderthals in the north of the Iberian Peninsula.
Written by Jan Bartek – AncientPages.com Staff Writer





