Jan Bartek – AncientPages.com – Prolonged drought likely helped to fuel civil conflict and the eventual political collapse of Mayapan, the ancient capital city of the Maya on the Yucatán Peninsula, suggests a new study in Nature Communications that was published with the help of a University at Albany archaeologist.

Ruins of the monumental center of Mayapan. Credit: Marilyn Mᴀsson
Mayapan served as the capital to some 20,000 Maya people in the 13th through mid-15th centuries but collapsed and was abandoned after a rival political faction, the Xiu, mᴀssacred the powerful Cocom family. Extensive historical records date this collapse to sometime between 1441 and 1461.
But new evidence shows drought in the century prior may have played a larger role in the city’s demise than was previously known. The study authors note this is relevant today as humans grapple with a future of increased climate change.
Marilyn Mᴀsson, an archaeologist and professor and chair of UAlbany’s Department of Anthropology, helped design and is a co-author of the study, which was ᴀssisted by an international team of interdisciplinary researchers. They studied historical documents for records of violence and examined human remains from that area and time period for signs of traumatic injury.
Mᴀsson, who serves as principal investigator for the Proyecto Económico de Mayapan, said she and the team found shallow mᴀss graves and evidence of brutal mᴀssacre at monumental structures across the city.
“Some were laid out with knives in their pelvis and rib cages, and other skeletal remains were chopped up and burned,” she said. “Not only did they smash and burn the bodies, but they also smashed and burned the effigies of their gods. It’s a form of double desecration basically.”
But that was hardly the most shocking discovery for the researchers.
That came when Douglas Kennett, the lead study author with the University of California Santa Barbara’s anthropology department, dated the skeletons using accelerator mᴀss spectrometry, an advanced form of radiocarbon dating technology, and found they dated some 50 to 100 years earlier than the city’s storied mid-15th century downfall.
“So then we started asking why? Because this is a case where archaeology reveals something that’s not told in history,” Mᴀsson said.
Plenty of ethnohistorical records exist to support the city’s violent downfall and abandonment around 1458, she said. But the new evidence of mᴀssacre up to 100 years earlier, together with climate data that found prolonged drought around that time, led the team to suspect environmental factors may have played a role.
Paleoclimate scientists were able to calculate annual rainfall levels from that period using a dating process that relied on calcite deposits in nearby caves, and found evidence of a drying trend throughout the 1300s. In particular, researchers found a significant relationship between a period of drought and substantial population decline from 1350 to 1430.
The Maya depended heavily on rain-fed maize but lacked any centralized long-term grain storage. The impacts of rainfall levels on food production, then, are believed to be linked to human migration, population decline, warfare and shifts in political power, the study states.
“It’s not that droughts cause social conflict, but they create the conditions whereby violence can occur,” Mᴀsson said.
The study authors suggest the Xiu, who launched the ultimate fatal attacks on the Cocom, used the droughts and ensuing famines to foment the unrest and rebellion that led to the mᴀss deaths and outmigration from Mayapan in the 1300s.
“I think the lesson is that hardship can become politicized in the worst kind of way,” Mᴀsson said. “It creates opportunities for ruthlessness and can cause people to turn on one another violently.”
Following this period of drought and unrest, however, the city appears to have bounced back briefly with the help of healthy rainfall levels around 1400, the authors wrote.
“Mayapan was able to bend pretty far and then bounce back before the droughts returned by the 1420s, but it was too soon,” Mᴀsson said. “They didn’t have enough time to recover, and the tensions were still there and the city’s government just couldn’t survive another bout like that. But it almost did.”
As food insecurity, social unrest and drought-driven migration in parts of the world continue to be of great concern, Mᴀsson said there are lessons in how other empires have handled environmental hardships.
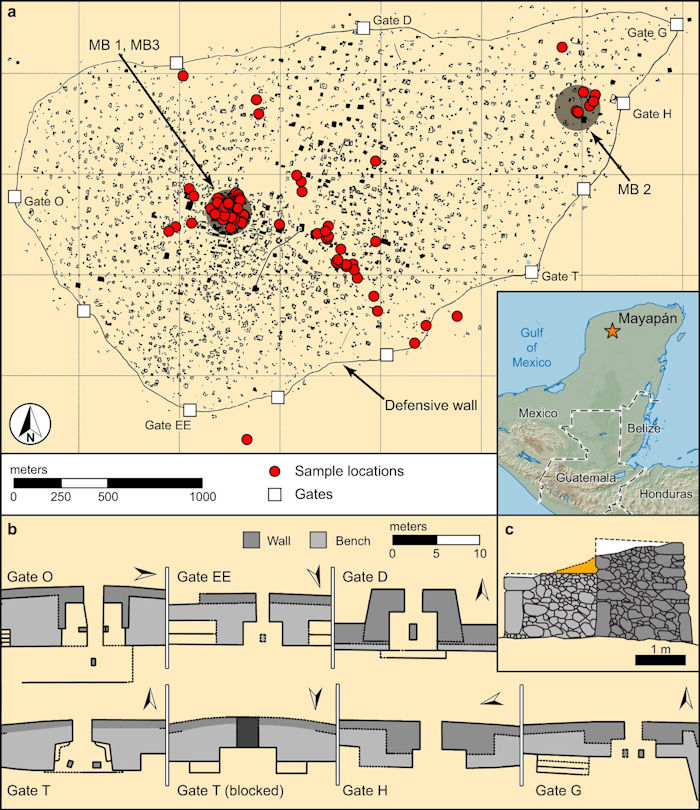
Map of Mayapan. a, Layout of the city showing housing complexes, the defensive wall, formal gates, and the locations of skeletal samples (red dots). b, Gate and wall configurations adapted from prior research. c, Cross-section of the tiered double-wall construction surrounding Mayapan. MB, Mᴀss Burial. Credit: Nature Communications (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-31522-x
The Aztec, for example, survived the infamous “Famine of One Rabbit,” which had been fueled by a catastrophic drought in the year 1454. The emperor emptied out stores of food from the capital to feed citizens and when that ran out, encouraged them to flee, Mᴀsson said. Many sold themselves into slavery on the Gulf Coast where conditions were better, but eventually bought their way out, returned to the capital, and the empire was stronger than ever.
This strategy enacted by the Aztec imperial regime is likely what allowed for their recovery, Mᴀsson said.
See also: More Archaeology News
“Overall, we argue that human responses to drought on the Yucatan Peninsula…were complex,” the study concludes. “On the one hand, drought stimulated civil conflict and insтιтutional failure at Mayapan. However, even after Mayapan fell, despite decentralization, intervals of mobility, temporary impacts to trade, and continuing military conflict, a resilient network of small Maya states persisted that were encountered by Europeans in the early 16th century. These complexities are important as we attempt to evaluate the potential success or failure of modern state insтιтutions designed to maintain internal order and peace in the face of future climate change.”
The study was published in Nature Communications
Written by Jan Bartek – AncientPages.com Staff Writer





