Conny Waters – AncientPages.com – Scientists have discovered surprising evidence modern humans successively inhabited the Mandrin Cave in France within an interval of barely a year.
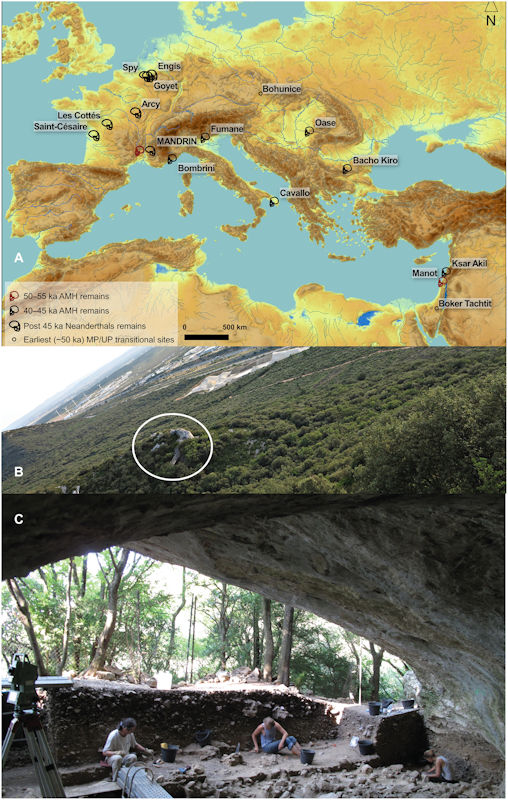
Studies of hominin fossils reveal modern humans reached the cave about 56,000 years ago which is 10,000 years earlier than previously thought. The finding reveals the earliest known presence of modern humans in Europe.

Credit: Adobe Stock – Gorodenkoff
According to the study published in the journal Science “determining the extent of overlap between modern humans and other hominins in Eurasia, such as Neanderthals and Denisovans, is fundamental to understanding the nature of their interactions and what led to the disappearance of archaic hominins. Apart from a possible sporadic pulse recorded in Greece during the Middle Pleistocene, the first settlements of modern humans in Europe.” have been constrained to ~45,000 to 43,000 years ago.”
This latest finding could change researchers’ understanding of homo sapiens’ journey to the European continent.
Paleoanthropologist Ludovic Slimak, one of the authors of the study has hailed the Mandrin cave as a truly historical place that holds vital clues about prehistoric European people.
Scientists report the Hominin fossils, comprising nine dental specimens, were found in situ in most of Mandrin’s representing a minimum of seven individuals.
The archeological and fossil evidence unearthed in the French cave provides evidence of an incursion of modern humans into Europe about 10 millennia earlier than previously identified, by groups that appear to have had major technological advantages over contemporaneous Neanderthal groups.
According to Clément Zanolli, a paleoanthropologist at the University of Bordeaux the Neanderthals and the Homo Sapiens were in the same territory, and therefore most likely met.

Clearly, a group of Homo sapiens evolving in the region could very well have come across their Neanderthal cousins while they were on their way to create a place to live inside the cave.
“Paleogenetics tells us that there are hybridizations”, continues Clément Zanolli, “and we ourselves have Neanderthal DNA. It is therefore good to know that there was contact between the two populations, and they did not kill each other. The Mandrin cave and its surroundings could be one of the places of this meeting, the first one in Europe. “In the Near and Middle East there are a few sites where the two groups are known to have lived”, but here “no site demonstrates the co-occurrence of human groups in the same place”.
Why the Rhône Valley became a destination point for the Homo Sapiens can be explained, according to Smilak by the fact Rhône is one of the largest rivers in Europe and the only pᴀssage from the Mediterranean side to continental Europe. Nomadic populations would have been forced to take the same path which would explain why they met.
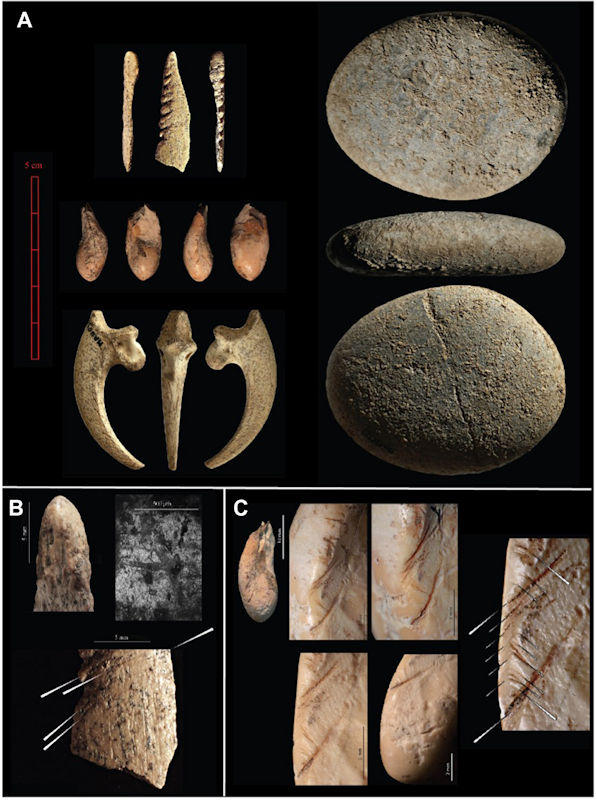
Some of the artifacts discovered inside the mandrin Cave. Credit: Ludovic Slimak, CNRS.
Among the objects unearthed inside the Mandrin Cave, scientists came across fine blades. These were sophisticated ancient tools produced with technology unknown to the Neanderthals. However, such tools have previously been found during excavations in Lebanon.
According to Slimak, this indicates the first Homo Sapiens arrived by maritime routes, which would explain the absence of tools of this kind in the caves of Greece or Italy.
See also: More Archaeology News
However, CNRS researcher Francesco d’Errico disagrees with this theory arguing the ancient tools discovered in the Middle East are different.
Nevertheless, d’Errico agrees the discovery of Hominin fossils in the Grotte Mandrin in France can re-write the ancient history of the first modern people in Europe. It is still however too early to say anything conclusive about the findings as more studies of the cave as well as the artifacts must be carried out.
Written by Conny Waters – AncientPages.com Staff Writer





