Jan Bartek – AncientPages.com – The riddle to solve the purpose of Stonehenge continues. It had long been thought that the famous site of Stonehenge served as an ancient calendar, given its alignment with the solstices. Now, research has identified how it may have worked.
New finds about the stone circle’s history, along with analysis of other ancient calendar systems, prompted professor Timothy Darvill to take a fresh look at Stonehenge. His analysis, published in the journal Antiquity, concluded that the site was designed as a solar calendar.

Stonehenge. Credit: Erwin Bosman – CC0 1.0
“The clear solsтιтial alignment of Stonehenge has prompted people to suggest that the site included some kind of calendar since the antiquarian William Stukeley,” said Darvill, from Bournemouth University, “Now, discoveries brought the issue into sharper focus and indicate the site was a calendar based on a tropical solar year of 365.25 days.”
Crucially, recent research had shown that Stonehenge’s sarsens were added during the same phase of construction around 2500 BC. They were sourced from the same area and subsequently remained in the same formation. This indicates they worked as a single unit.
As such, Darvill analyzed these stones, examining their numerology and comparing them to other known calendars from this period. He identified a solar calendar in their layout, suggesting they served as a physical representation of the year that helped the ancient inhabitants of Wiltshire keep track of the days, weeks, and months.
“The proposed calendar works in a very straightforward way. Each of the 30 stones in the sarsen circle represents a day within a month, itself divided into three weeks each of 10 days,” said Darvill, noting that distinctive stones in the circle mark the start of each week.
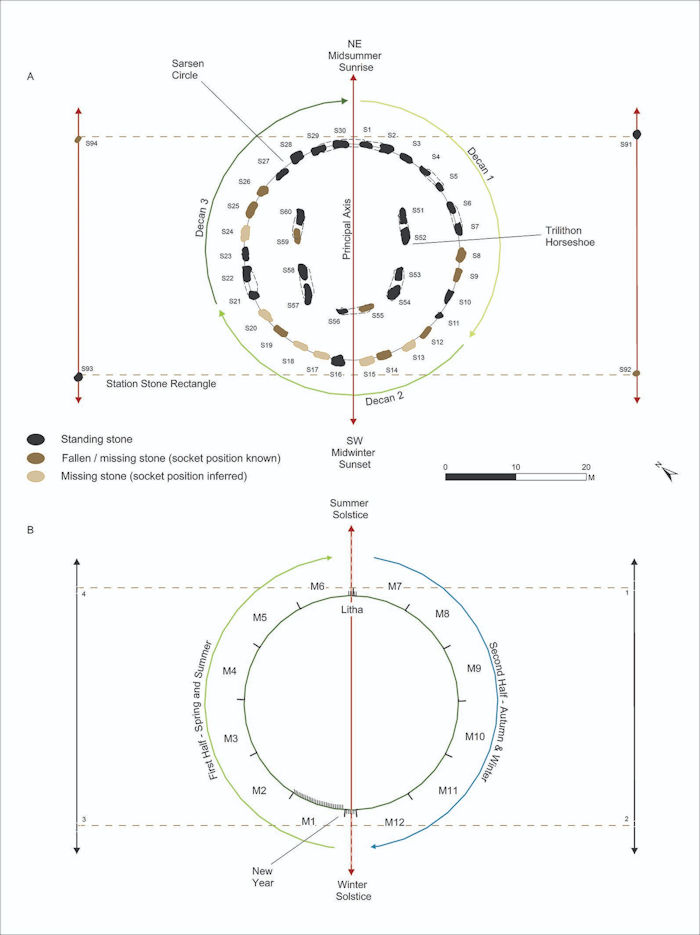
Credit: Antiquity (2022). DOI: 10.15184/aqy.2022.5
Additionally, an intercalary month of five days and a leap day every four years were needed to match the solar year. “The intercalary month, probably dedicated to the deities of the site, is represented by the five trilithons in the center of the site,” said Darvill. “The four Station Stones outside the Sarsen Circle provide markers to notch-up until a leap day.”
As such, the winter and summer solstices would be framed by the same pairs of stones every year. One of the trilithons also frames the winter solstice, indicating it may have been the new year. This solsтιтial alignment also helps calibrate the calendar—any errors in counting the days would be easily detectable as the sun would be in the wrong place on the solstices.
Such a calendar, with 10 day weeks and extra months, may seem unusual today. However, calendars like this were adopted by many cultures during this period.
“Such a solar calendar was developed in the eastern Mediterranean in the centuries after 3000 BC and was adopted in Egypt as the Civil Calendar around 2700 and was widely used at the start of the Old Kingdom about 2600 BC,” said Darvill. This raises the possibility that the calendar tracked by Stonehenge may stem from the influence of one of these other cultures. Nearby finds hint at such cultural connections—the nearby Amesbury archer, buried nearby around the same period, was born in the Alps and moved to Britain as a teenager.
See also: More Archaeology News
Professor Darvill hopes future research might shed light on these possibilities. Ancient DNA and archaeological artifacts could reveal connections between these cultures. Nevertheless, the identification of a solar calendar at Stonehenge should transform how we see it.
“Finding a solar calendar represented in the architecture of Stonehenge opens up a whole new way of seeing the monument as a place for the living,” he said, “a place where the timing of ceremonies and festivals was connected to the very fabric of the universe and celestial movements in the heavens.”
Written by Jan Bartek – AncientPages.com Staff Writer





