Conny Waters – AncientPages.com – Archaeologists examining the Herculaneum skeletal remains of the victims of Vesuvius that erupted on the morning of August 24, 79 AD, and broke its centuries-long silence.
Now, researchers say their study has helped shed new light on the eating habits of ancient Romans – with food differentiated along gender lines and revealing women ate more animal products and locally grown fruit and vegetables while the men dined on more expensive fish.
In 79 AD, Vesuvius erupted and completely buried the Roman cities of Pompeii and Herculaneum, on the coast of southwest Italy. For a long time, both cities have remained forgotten, sealed, and preserved in a time capsule.
Researchers – led by the University of York’s BioArCh team – developed a new approach to analyze amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, from 17 adult skeletons found in the aftermath of the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 AD.
By measuring the isotopes of carbon and nitrogen in the bone amino acids, the researchers were able to reconstruct the diets of people who lived contemporaneously in much more detail than was previously thought possible.
See also:
Herculaneum Time Capsule: Ancient Scrolls With Secrets Buried Under Volcanic Ash And Stones
Senior author, Professor Oliver Craig, the Director of BioArCH from the Department of Archaeology, said that “the remains of those who perished at Herculaneum in AD79 offer a unique opportunity to examine the lifestyles across an ancient community who lived and died together. Historical sources often allude to differential access to foodstuffs across Roman society but rarely provide direct or quanтιтative information.
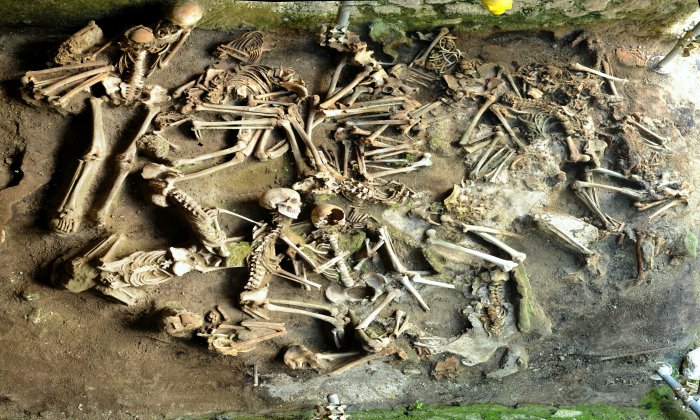 Scientists looked at skeletons found in the aftermath of the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 AD. Image credit: Dr. Luciano Fattore
Scientists looked at skeletons found in the aftermath of the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 AD. Image credit: Dr. Luciano Fattore
“We found significant differences in the proportions of marine and terrestrial foods consumed between males and females, implying that access to food was differentiated according to gender.”
In total, 340 individuals have been excavated from the beach and from nine adjacent fornici (stone vaults) that run parallel to the seashore in Herculaneum, near Pompeii, where people sought shelter from the pyroclastic flow.
Researchers said they were able to quantify the gender gap more accurately within the group, with males on average obtaining approximately 50 percent more of their dietary protein from seafood compared with females.
Males also obtained a slightly higher proportion of protein from cereals compared with their female contemporaries, whereas females obtained a greater proportion of protein from animal products and locally grown fruits and vegetables.
“Our research builds on what we know that males had greater access to marine fish at Herculaneum and more broadly in Roman Italy,” lead author, Ph.D. student Silvia Soncin, from the Department of Archaeology, said.
“Males were more likely to be directly engaged in fishing and maritime activities, they generally occupied more privileged positions in society, and were freed from slavery at an earlier age providing greater access to expensive commodities, such as fresh fish.”
Using their new approach, the researchers were able to more accurately quantify ancient diets so they could be compared with recent nutritional records.
The team suggests that fish and seafood made a greater overall contribution to the diets at Herculaneum compared to the average modern Mediterranean diet; the latter is increasingly dominated by animal products. Whereas a similar proportion of cereals were consumed between ancient and modern.
Paper
Written by Conny Waters – AncientPages.com Staff Writer





