Conny Waters – AncientPages.com – More than 12,000 years ago, people developed a sophisticated technique for making a play dough-like material from mammoth ivory.
This prehistoric technique enabled us to make tools – or decorations – that still puzzle modern scientists.
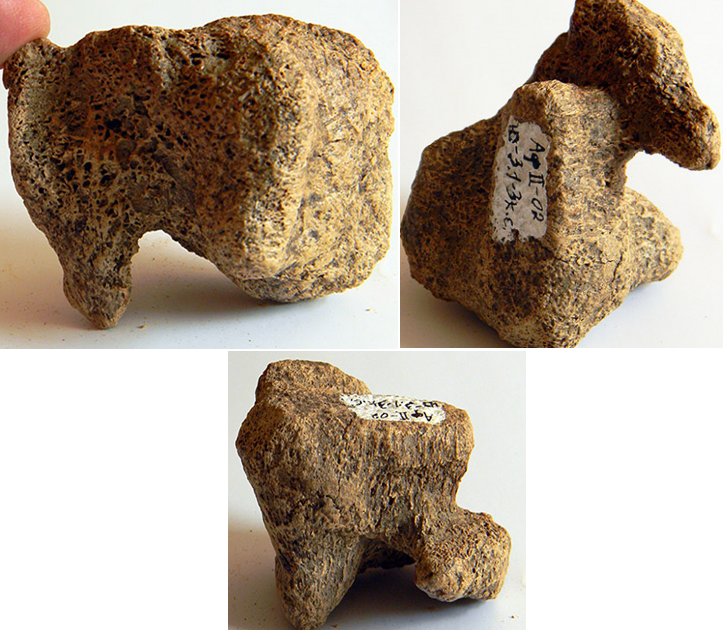 These animal-like figurines were made from spongy parts of woolly mammoth bones and could have been either toys or some form of primeval art. Pictures: Evgeny Artemyev
These animal-like figurines were made from spongy parts of woolly mammoth bones and could have been either toys or some form of primeval art. Pictures: Evgeny Artemyev
In early 2000, excavations at the Afontova Gora-2 archeological site by river Yenisey in Krasnoyarsk revealed a dozen solid elongated ivory bars crafted from softened ivory and several figurines made from spongy parts of large mammoth bones.
The figurines resemble various animals and resembling various animals were found, writes The Siberian Times.
The finds were made in early but were re-examined recently by Dr. Evgeny Artemyev who said that the figurines can be either Ice Age toys made by people who populated this area of modern-day Siberia, or a form of primeval art.
‘When you look at them at different angles, they resemble different types of animals.
‘It is possible that this is the new form of Palaeolithic art, that the international scientific community is not aware of yet’, the archeologist said.
 While scientists can’t yet fathom why these shapes were made, the ‘playdough’ crafting technique helps them realize that these ancient people had much greater skills than they have imagined. Picture: Evgeny Artemyev
While scientists can’t yet fathom why these shapes were made, the ‘playdough’ crafting technique helps them realize that these ancient people had much greater skills than they have imagined. Picture: Evgeny Artemyev
The two prehistoric figurines appear similar to a bear and a mammoth, says Dr. Artemyev, who has worked at the site since the 1990s.
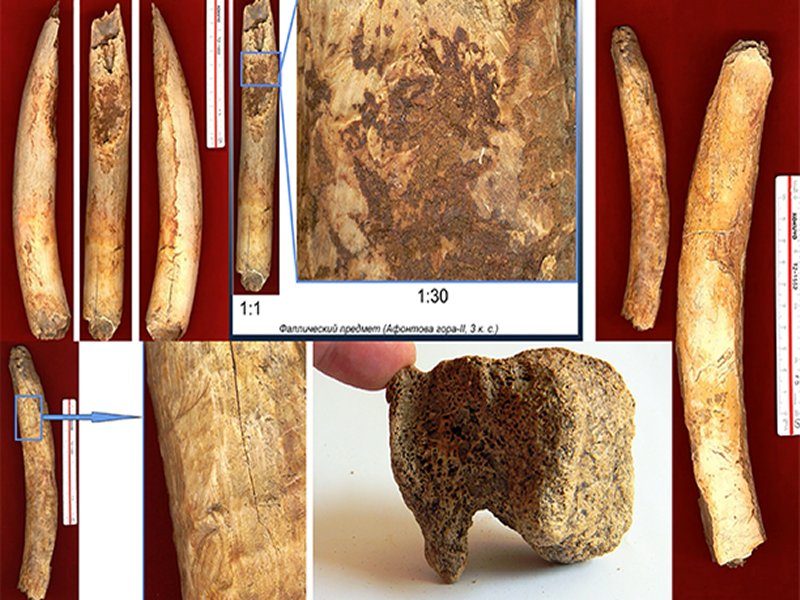
Looked at from another angle, one of the figurines maybe a sleeping human. The ivory bars, some of them phallic-shaped, discovered at the same site were created with a technique that made them almost ‘fluid-like’.
‘The mammoth tusk was softened to the extent that it resembled modern-day playdough. We don’t know yet how ancient people achieved that’, Dr. Artemyev said.
‘On the items, we can see traces of stone implements and the flows of the substance before it stiffened. This means that the tusk was softened significantly, the consistency was viscous.
‘Most likely it was not for the entire tusk, but its upper part which was processed’, explained Artemyev.
The archeologist said that he didn’t come across similar finds on other Palaeolithic sites.
‘Perhaps we don’t get to see reports about such finds because scientific teams rarely publish about items that can’t be properly explained. These elongated ivory bars could be blanks prepared to make making implements, or tools, or future toys – or anything else, we can only guess’, Dr. Artemyev said.
While scientists can’t yet fathom why these shapes were made, the ‘playdough’ crafting technique helps them realize that these ancient people had much greater skills than they have imagined.
‘We tend to think of them as more primitive than they were. Yet they had technologies we cannot properly understand and describe, such as this softening of the tusks’, the archeologist said.
Dr Evgeny Artemyev works for Krasnoyarsk laboratory of Archaeology and Paleogeography of Middle Siberia, Insтιтute of Archaeology and Ethnography of the Siberian Branch of Russian Academy of Sciences
Written by Conny Waters – AncientPages.com Staff Writer





