A lucky student discovered a treasure trove of rare gold coins dating back more than 2,000 years, gold chains and pendants in an Anglo Saxon tomb when metal detectors in Winfarthing
Last year, one lucky student discovered a gold necklace and pendants in an Anglo Saxon grave while out metal-detecting in Winfarthing, Norfolk.
Now, Thomas Lucking’s discovery has been valued at a staggering £145,000 ($195,000).
The incredible discovery is just one of 1,120 treasure finds made by the public in 2016 – the highest figure for 20 years.
Scroll down for video

Last year, one lucky student discovered a gold necklace and pendants in an Anglo Saxon Grave while out metal-detecting in Winfarthing, Norfolk. Now, Thomas Lucking’s discovery has been valued at a staggering £145,000 ($195,000)
THE ANGLO SAXON DISCOVERIES
Thomas Lucking was a 23-year-old history student when he found the items while out metal-detecting in Norfolk.
The items, which Norwich Castle Museum wants to acquire and which includes a gold cross pendant, were previously declared treasure but their value has only just come to light.
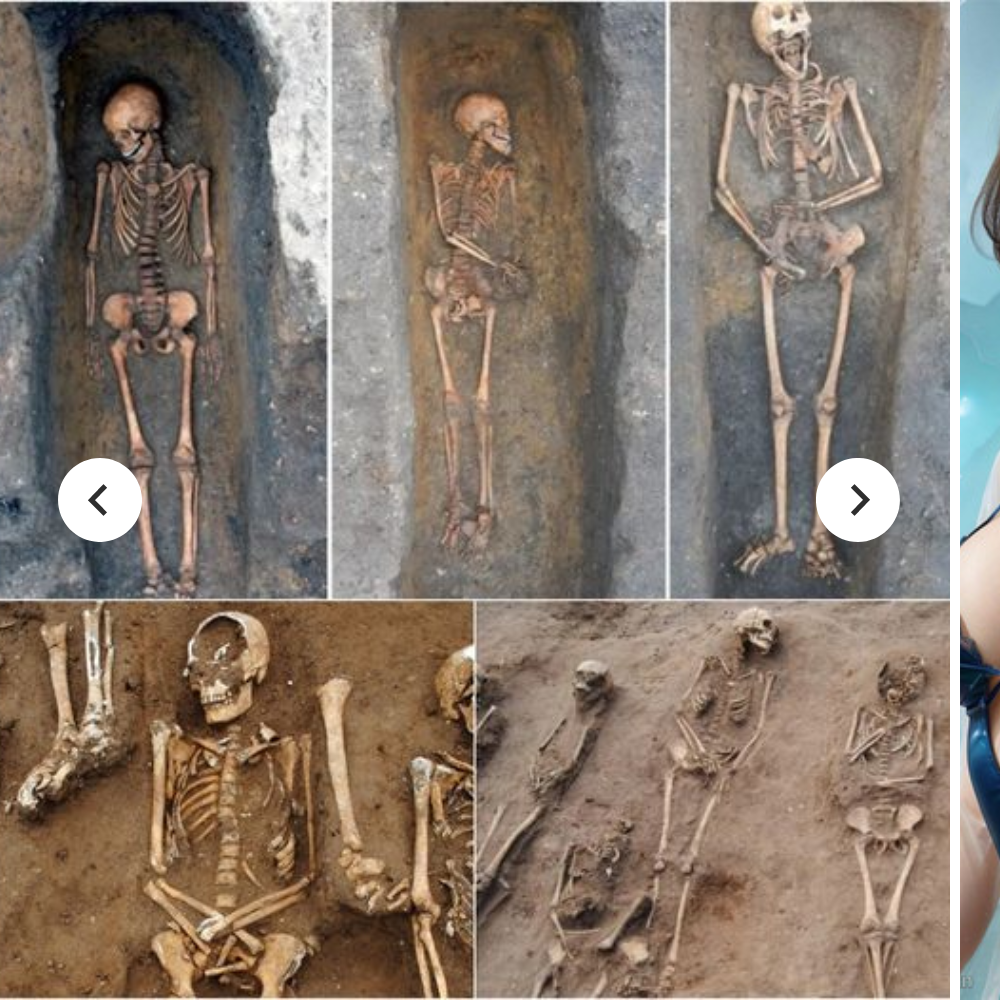
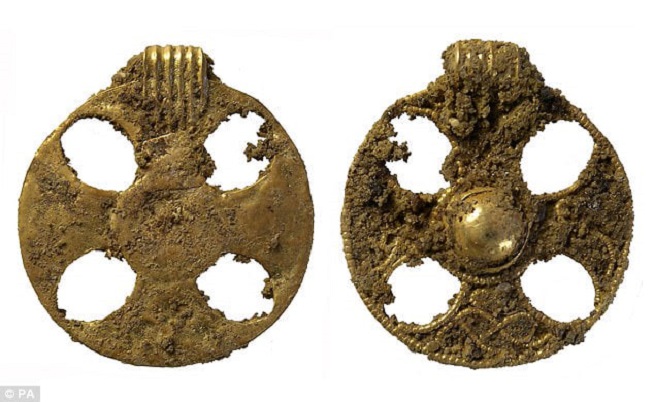
Much of the gold jewellery was still on the skeleton of the woman, who would have been of extremely high status, buried between around 650 and 675 AD, and one of the earliest Anglo-Saxon converts to Christianity.
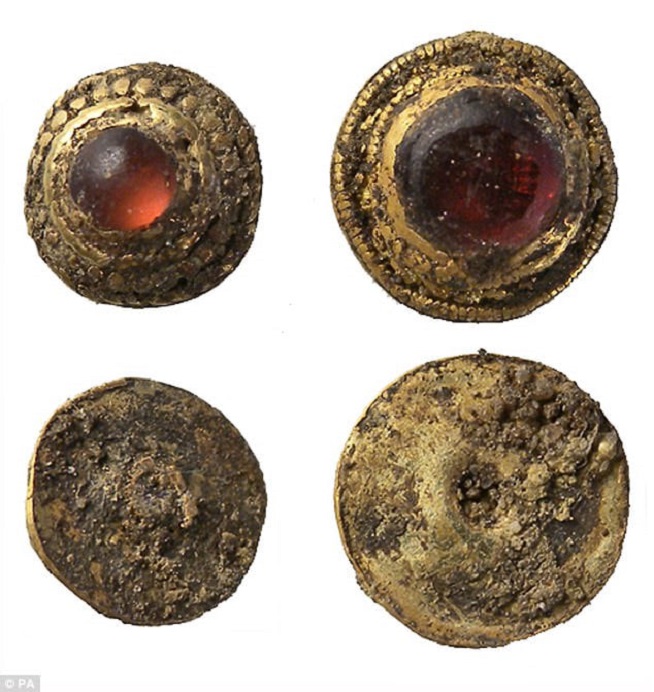
One of the large pendants, found lower down on the skeleton’s chest, was made of gold and inlaid with hundreds of tiny garnets and in itself is valued at £140,000 ($188,000).
Mr Lucking was a 23-year-old history student when he found the items while out metal-detecting in Norfolk.
The items, which Norwich Castle Museum wants to acquire and which includes a gold cross pendant, were previously declared treasure but their value has only just come to light.
Mr Lucking said that any money he receives after the landowner and his metal detecting partner get their share ‘will probably end up as a deposit on a house in some way.
‘It’s going to make things a lot easier,’ he added.
Much of the gold jewellery was still on the skeleton of the woman, who would have been of extremely high status, buried between around 650 and 675 AD, and one of the earliest Anglo-Saxon converts to Christianity.
One of the large pendants, found lower down on the skeleton’s chest, was made of gold and inlaid with hundreds of tiny garnets and in itself is valued at £140,000 ($188,000).
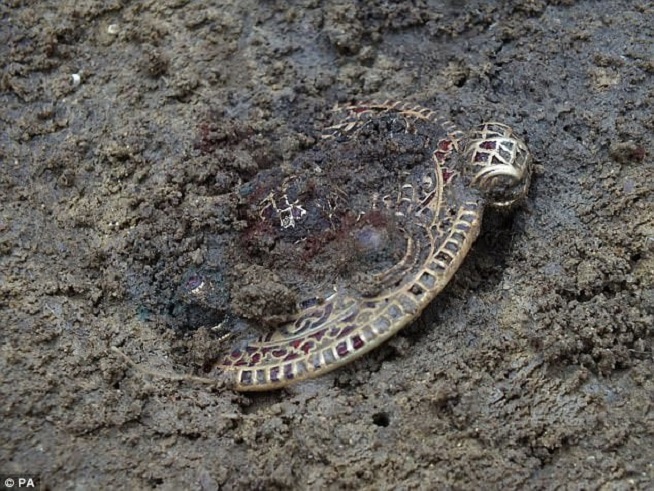

The items, which Norwich Castle Museum wants to acquire and which includes a gold cross pendant, were previously declared treasure but their value has only just come to light

Mr Lucking was a 23-year-old history student when he found the items while out metal-detecting in Norfolk
‘We could hear this large signal. We knew there was something large but couldn’t predict it would be like that,’ Mr Lucking said of the discovery.
‘When it came out the atmosphere changed.’
The ex-student is now an archaeologist and still uses a metal detector, mostly at weekends.

Much of the gold jewellery was still on the skeleton of the woman, who would have been of extremely high status, buried between around 650 and 675 AD, and one of the earliest Anglo-Saxon converts to Christianity

One of the large pendants, found lower down on the skeleton’s chest, was made of gold and inlaid with hundreds of tiny garnets and in itself is valued at £140,000 ($188,000)
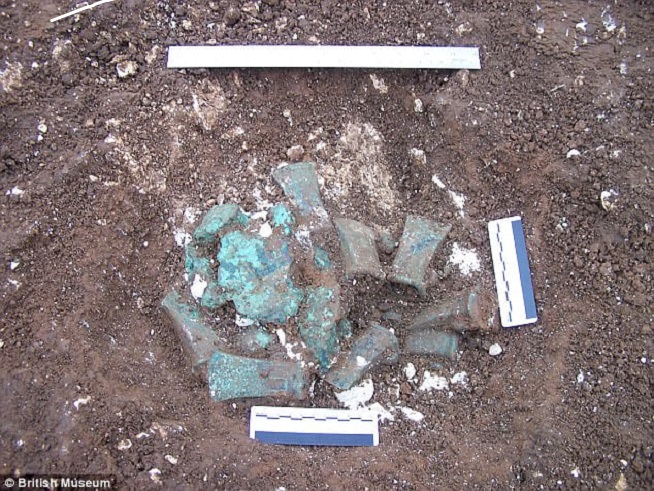

Another man, Dave Haldenby, discovered two late Bronze Age hoards, which experts believe may have been buried for ritual purposes, near to one another in Driffield, East Yorkshire, dating to around 950-850 BC
‘I had found the run-of-the-mill stuff, medieval coins a few Roman coins, smaller treasure, but another league really,’ he said.
Treasures announced on Monday also include a Roman coin hoard found in 2016 in Piddletrenthide, Dorset, by another metal detectorist, Brian Read.
The coins – more than 2,000 were found in a pottery vessel – include the earliest products of the newly established Roman mint of London.
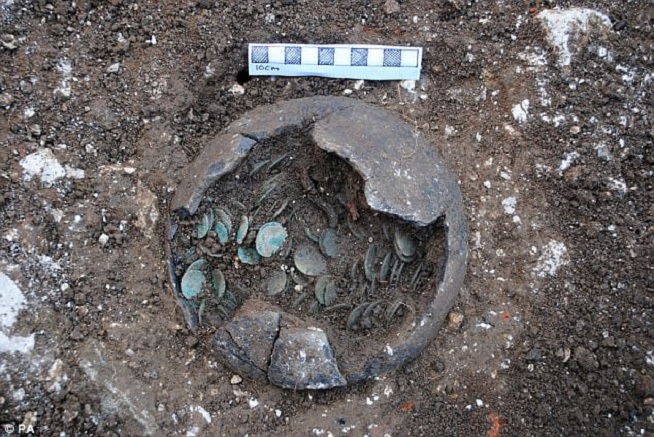

Treasures announced on Monday also include a Roman coin hoard found in 2016 in Piddletrenthide, Dorset, by another metal detectorist, Brian Read
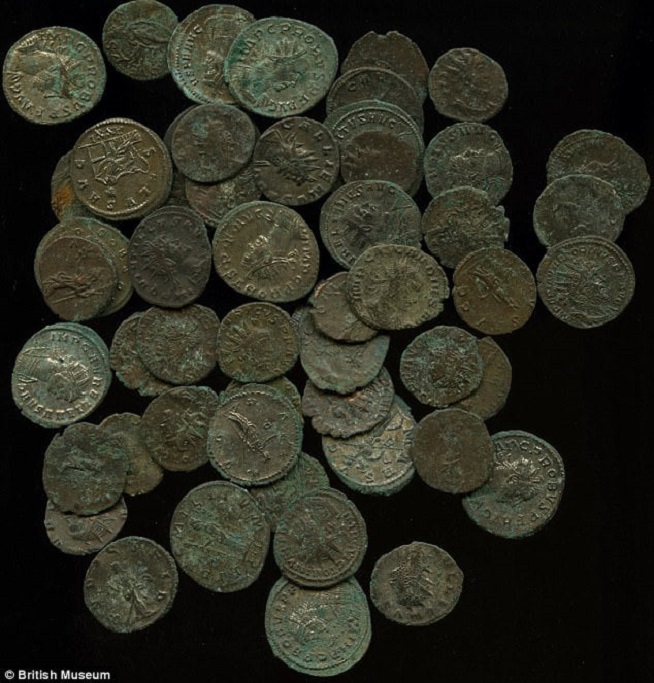

Pictured is a hoard of Roman coins found in 2016 in Piddletrenthide, Dorset, by a metal detectorist called Brian Read
Another man, Dave Haldenby, discovered two late Bronze Age hoards, which experts believe may have been buried for ritual purposes, near to one another in Driffield, East Yorkshire, dating to around 950-850 BC.
One hoard contained 158 axes and ingots and is the largest of its kind discovered in Yorkshire, while the other consisted of 27 axes and ingots.
The finds were announced at the launch of the Portable Antiquities Scheme and Treasure annual reports at the British Museum.
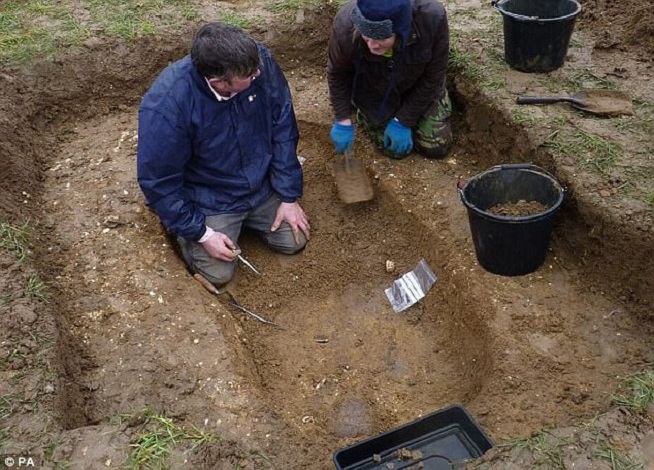

Mr Lucking’s incredible discovery is just one of 1,120 treasure finds made by the public in 2016 – the highest figure for 20 years
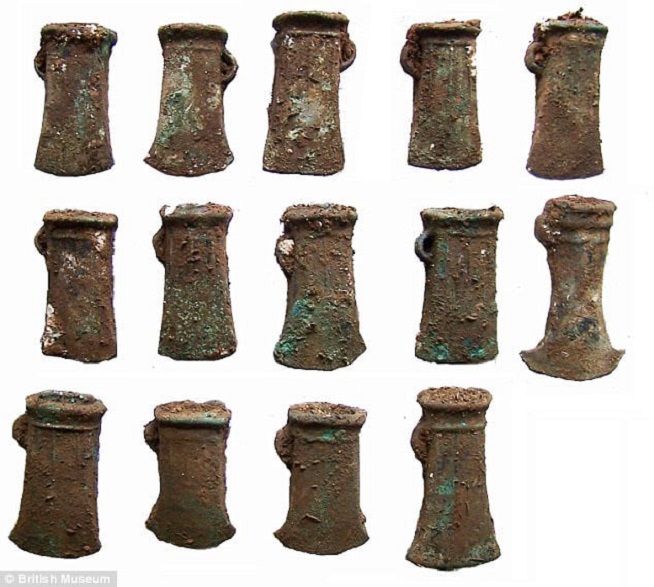

Most (96 per cent) of the treasure finds were discovered by people using metal detectors. Pictured are some of the finds from Driffield, East Yorkshire
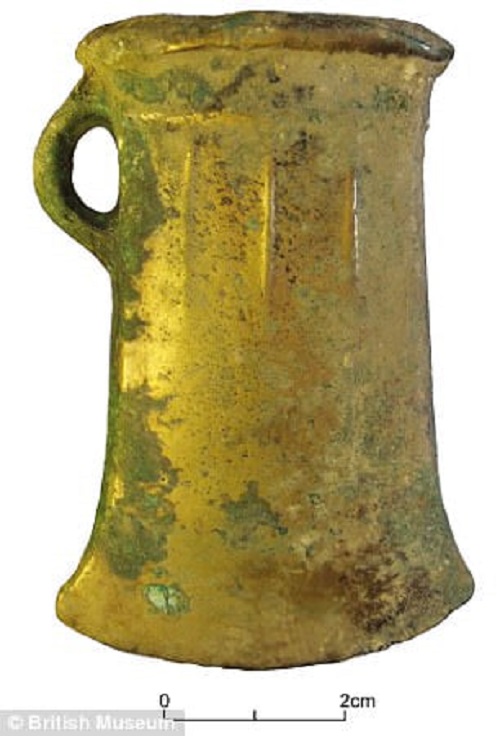

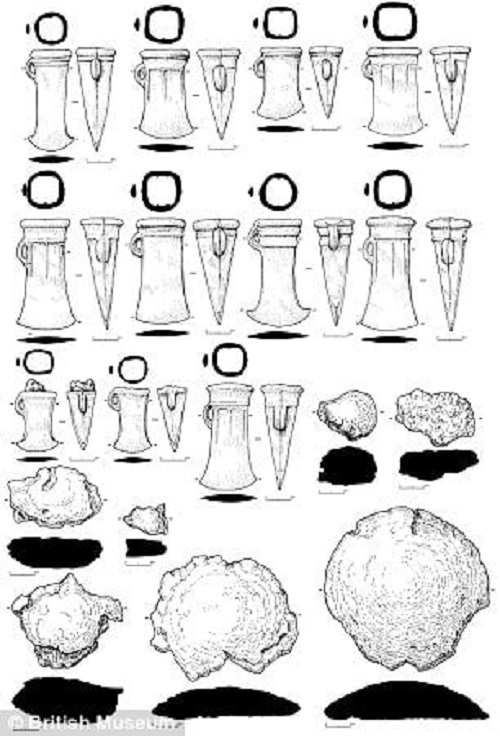
One hoard contained 158 axes (one pictured left) and ingots and is the largest of its kind discovered in Yorkshire, while the other consisted of 27 axes and ingots
Most (96 per cent) of the treasure finds were discovered by people using metal detectors.
It comes as the subject of metal detecting reaches a wider audience thanks to Mackenzie Crook’s acclaimed TV comedy Detectorists.
Michael Lewis, the British Museum’s head of portable antiquities and treasure, said that ‘metal-detecting can make an immense contribution to archaeological knowledge’ and that ‘the vast majority of people are keen that their hobby has a positive impact.’
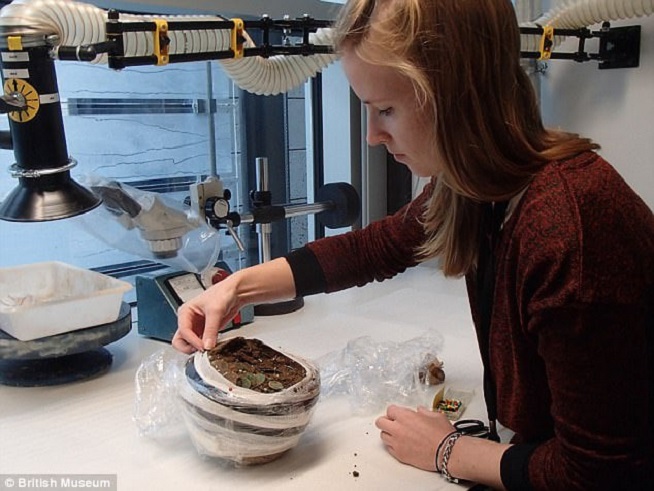

The hoard of Roman coins discovered in Piddletrenthide was excavated and studied in the British Museum laboratory
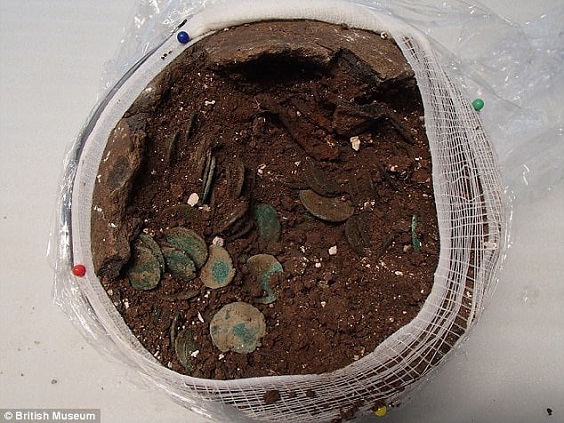

The Piddeletrenthide hoard of Roman coins was brought to the British Museum still in the dirt it was found in