Conny Waters – AncientPages.com – The human middle ear—which houses three tiny, vibrating bones—is key to transporting sound vibrations into the inner ear, where they become nerve impulses that allow us to hear.

The 3D braincase of Shuyu. Credit: IVPP
Embryonic and fossil evidence proves that the human middle ear evolved from the spiracle of fishes. However, the origin of the vertebrate spiracle has long been an unsolved mystery in vertebrate evolution.
Some 20th century researchers, believing that early vertebrates must possess a complete spiracular gill, searched for one between the mandibular and hyoid arches of early vertebrates. Despite extensive research spanning more than a century, though, none were found in any vertebrate fossils.
Now, however, scientists from the Insтιтute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology (IVPP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and their collaborators have found clues to this mystery from armored galeaspid fossils in China.
According to Prof. Gai Zhikun from IVPP, first author of the study, researchers from the insтιтute successively found over the last 20 years a 438-million-year-old Shuyu 3D braincase fossil and the first 419-million-year-old galeaspid fossil completely preserved with gill filaments in the first branchial chamber. The fossils were found in Changxing, Zhejiang Province and Qujing, Yunnan Province, respectively.
“These fossils provided the first anatomical and fossil evidence for a vertebrate spiracle originating from fish gills,” said Gai.
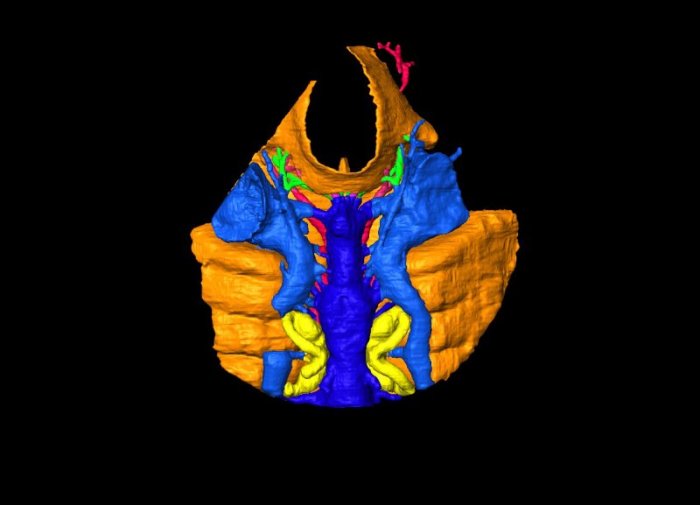
The 3D virtual reconstruction of Shuyu. Credit: IVPP
A total of seven virtual endocasts of the Shuyu braincase were subsequently reconstructed. Almost all details of the cranial anatomy of Shuyu were revealed in its fingernail-sized skull, including five brain divisions, sensory organs, and cranial nerve and blood vessel pᴀssages in the skull.
“Many important structures of human beings can be traced back to our fish ancestors, such as our teeth, jaws, middle ears, etc. The main task of paleontologists is to find the important missing links in the evolutionary chain from fish to humans. Shuyu has been regarded as a key missing link as important as Archaeopteryx, Ichthyostega and Tiktaalik,” said Zhu Min, academician of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
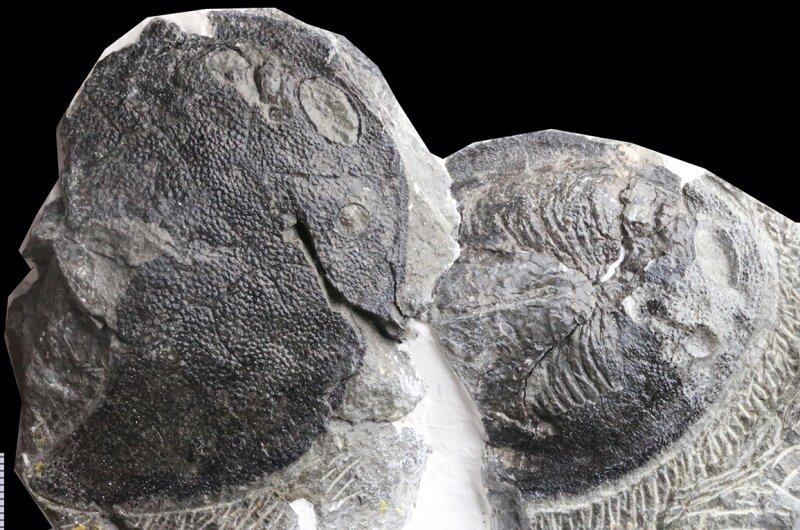

The first 419-million-year-old galeaspid fossil completely preserved with gill filaments in the first branchial chamber. Credit: IVPP
The spiracle is a small hole behind each eye that opens to the mouth in some fishes. In sharks and all rays, the spiracle is responsible for the intake of water into the buccal space before being expelled from the gills. The spiracle is often located towards the top of the animal allowing breathing even while the animal is mostly buried under sediment.
In the Polypterus, the most primitive, living bony fish, the spiracles are used to breathe air. However, fish spiracles were eventually replaced in most non-fish species as they evolved to breathe through their noses and mouths. In early tetrapods, the spiracle seems to have developed first into the Otic notch. Like the spiracle, it was used in respiration and was incapable of sensing sound.
Later the spiracle evolved into the ear of modern tetrapods, eventually becoming the hearing canal used for transmitting sound to the brain via tiny inner ear bones. This function has remained throughout the evolution to humans.
“Our finding bridges the entire history of the spiracular slit, bringing together recent discoveries from the gill pouches of fossil jawless vertebrates, via the spiracles of the earliest jawed vertebrates, to the middle ears of the first tetrapods, which tells this extraordinary evolutionary story,” said Prof. Per E. Ahlberg from Uppsala University and academician of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences.
Paper
Written by Conny Waters – AncientPages.com Staff Writer





