Conny Waters – AncientPages.com – The theory that iron technology was a late introduction, pᴀssively received by the population in communities of the Circumpolar North, was finally challenged.
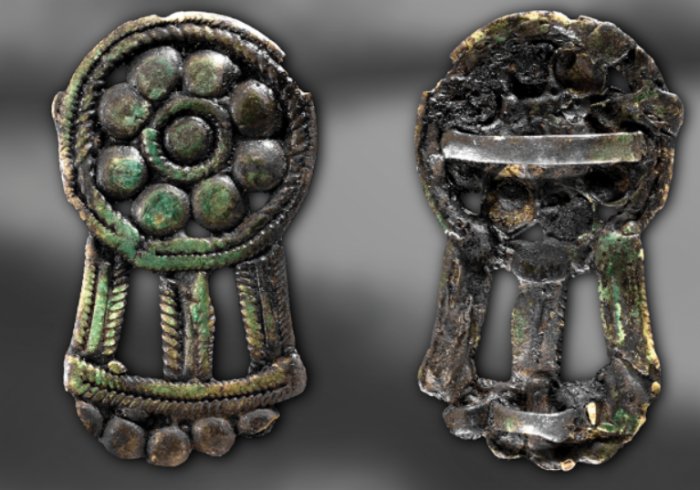

Bronze buckle (F1784) from the Sangis smithing site (Sangis 730). Charred organic material (resin?) was found next to the bronze buckle, radiocarbon-dated to c. 50 BC–AD 115 (Poz 23733) (pH๏τograph by S. Nygren © Norrbottens Museum).
Traditionally, it was believed these hunter-gatherer societies had insufficiently developed iron production. According to the widespread diffusion model, iron technology began as a single invention in the Near East in the second millennium BC.
There was also lack of research that limited our understanding of early iron technology in the region. In other words – the topic was long time neglected.
New groundbreaking and extensive evidence shows thatiron tec hnology among these societies was not underdeveloped but rather an integrated and advanced technology in hunter-gatherer societies in Northern Fennoscandia during the pre-Roman Iron Age (c. 200–50 BC).
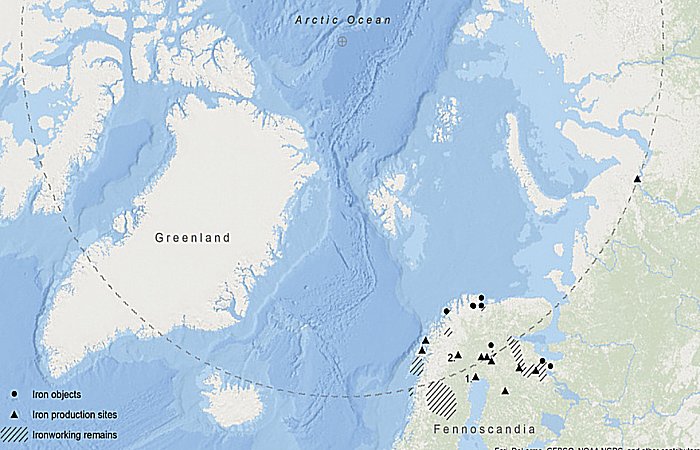
Published iron objects and metalworking remains in the Circumpolar North from the Late Bronze Age to the beginning of the first millennium AD: 1) the Sangis site (Sangis 730 and 842); 2) the Vivungi site (Vivungi 723) (figure by C. Bennerhag © Norrbottens Museum).
Findings from Vivungi and Sangis excavated sites in northernmost Sweden delivered this evidence.
Researchers conducted archaeometallurgical analyses of these sites’ metallurgical remains. They found no signs of any experiments, which means the knowledge (both practical and theoretical) has been transferred to these ancient people as a full package. The ability of metallurgy originated from highly skilled metal workers from other areas, like, for example, Finland and Russian Karelia.
Many iron objects have been found in Northern Fennoscandia (i.e., the Scandinavian and Kola peninsulas, Finland and Karelia), the Russian Arctic, and the Bering Strait region.
These sites have yet to be subjected to archaeometallurgical analyses except for a few chemical analyses of slag, and the use of iron was only interpreted as small-scale for domestic use.
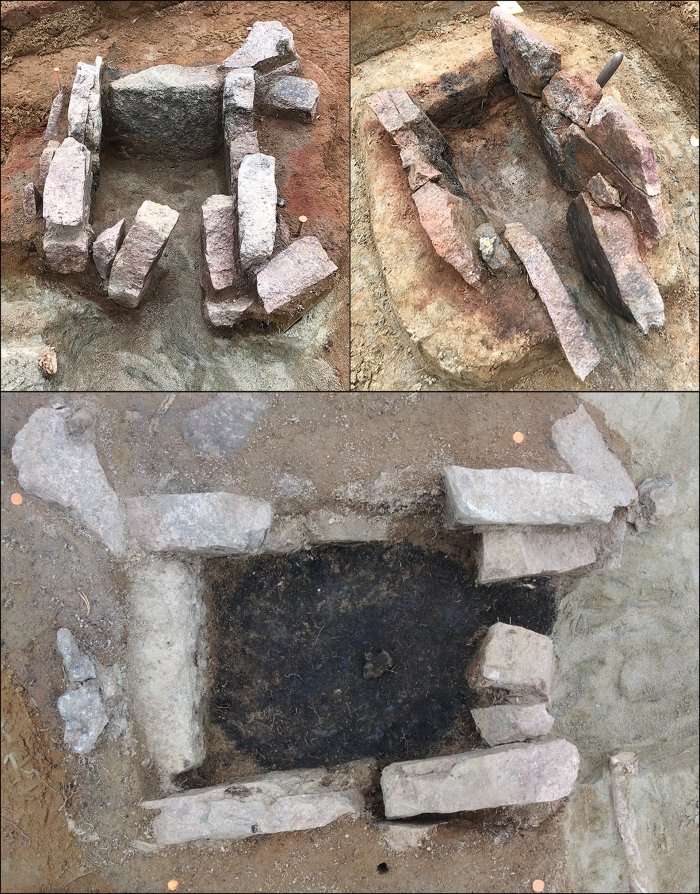

The bloomery furnaces at the Vivungi site (Vivungi 723) (left: furnace two; right: furnace three). A charcoal feature was found inside furnace two (bottom), showing that the inner part of the furnace shaft was oval (pH๏τographs by C. Bennerhag © Norrbottens Museum).
The sites of Sangis and Vivungi are located in the Arctic and Boreal zone of north-eastern Sweden: Sangis lies close to Lake Storträsket in the coastal area of the Bothnian Bay and Vivungi in the interior, approximately 140km north of the Arctic Circle.
In 2006–2007 and 2010, rescue excavations in advance of a railway expansion, and researchers found an iron-smelting site (Sangis 842) and a hunter-gatherer habitation site (Sangis 730), with smithing of iron objects.
The excavations revealed one bloomery furnace, debris from iron smelting, technical ceramics, and iron waste. Radiocarbon analyses showed that iron production occurred between c. 200 and 50 BC.
The hunter-gatherer habitation site (Sangis 730) yielded archaeological finds dating from the pre-Roman Iron Age to the Viking Age (c. 500 BC–AD 900).
“More than 50 features were identified, consisting of household and smithing hearths and cooking pits, along with large quanтιтies of lithic debitage, ceramic fragments, metallurgical finds and debris (iron and copper alloys), and faunal remains. “… the inhabitants’ diet was dominated by freshwater fish in all phases, emphasising the importance of aquatic resources. The faunal remains also include small game mammals (hare, marten and squirrel) and fragments of worked antler (probably from reindeer), indicating crafts such as the handling of furs and horn working. Evidence for smithing activities was concentrated in the central part of the habitation site, and consisted of five features, including at least three smithing hearths; the ᴀssociated ᴀssemblage comprised plano-convex slags, hammerscale, iron waste and several finished and semi-finished items of iron and steel…” write researchers in their paper
The excavations at the Vivungi site were carried out in 2017 by researchers from Luleå University of Technology in northern Sweden, in collaboration with archaeologists from the Sangis excavations and archaeometallurgists at the Swedish National Historical Museums.
Excavations revealed the remains of two bloomery furnaces (furnaces two and three, approximately 30m apart. These yielded smelting slag, technical ceramics, and iron ore and waste. Unlike the Sangis site, no evidence of smithing activities was found.
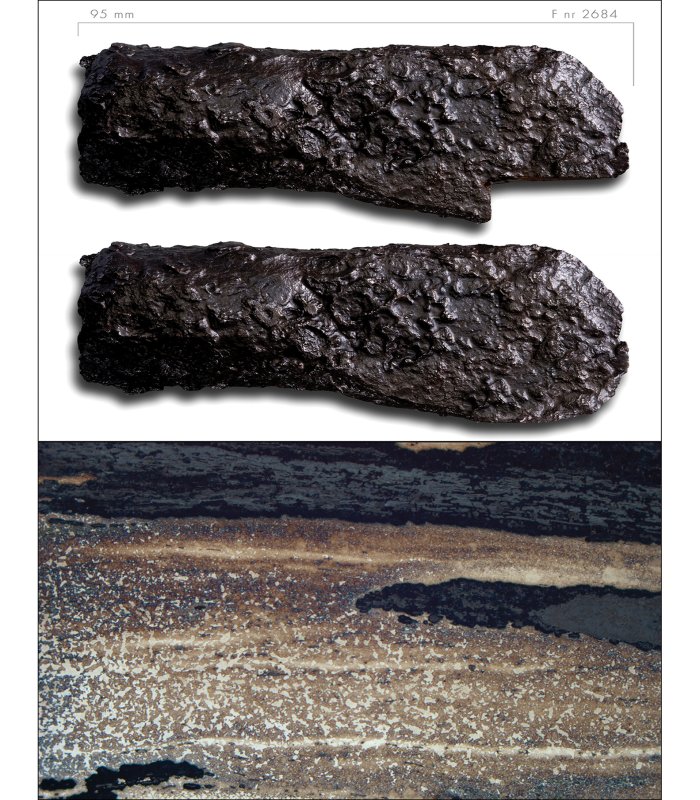

Socketed axe from the Sangis smithing site (Sangis 730) with a multi-layered structure indicating steel. The micrograph cross-section shows light lines indicating welding seams (pH๏τograph by S. Nygren © Norrbottens Museum; micrograph by L. Grandin © The Archaeologists, Swedish National Historical Museums).
Radiocarbon analyses of furnace remains, charcoal embedded within slag, and carbon extracted from iron (steel) waste indicate that iron production started at Vivungi around 100 BC, with overlapping dates around 50 BC–AD 50 .
Cutting-edge technology
“The Sangis and Vivungi sites reveal the inhabitants’ advanced knowledge of metallurgy. At an early stage, different types of iron, including soft ferritic iron and high-carbon steel, were produced. The numerous finds of high-quality steel waste at both sites indicate that smelting processes at high temperatures had been mastered, including the use of extreme temperatures in the furnaces, as attested by the presence of cast iron.
“Combined, this evidence suggests that the smelters were aware of the refractory properties of clays, as it is critical to maintain the structural stability of the furnace shaft during the high-temperature smelting process.
“… the smelters were well acquainted with a variety of raw materials and aware of their properties…” the paper states.
Research paper was published in Antiquity.
Written by Conny Waters – AncientPages.com Staff Writer





