The BRDM-2, an acronym for “Boyevaya Razvedyvatelnaya Dozornaya Mashina 2,” translates to “Combat Reconnaissance Patrol Vehicle 2” in English. This remarkable armored scout vehicle, hailing from the Soviet Union, has long been an integral part of military arsenals across the globe. With its robust design and impressive versatility, the BRDM-2 has gained recognition for its role in reconnaissance, patrol, and support missions. In this article, we will delve into the capabilities, history, and significance of the BRDM-2, showcasing the enduring legacy of this remarkable armored vehicle.
The BRDM-2: A Brief History
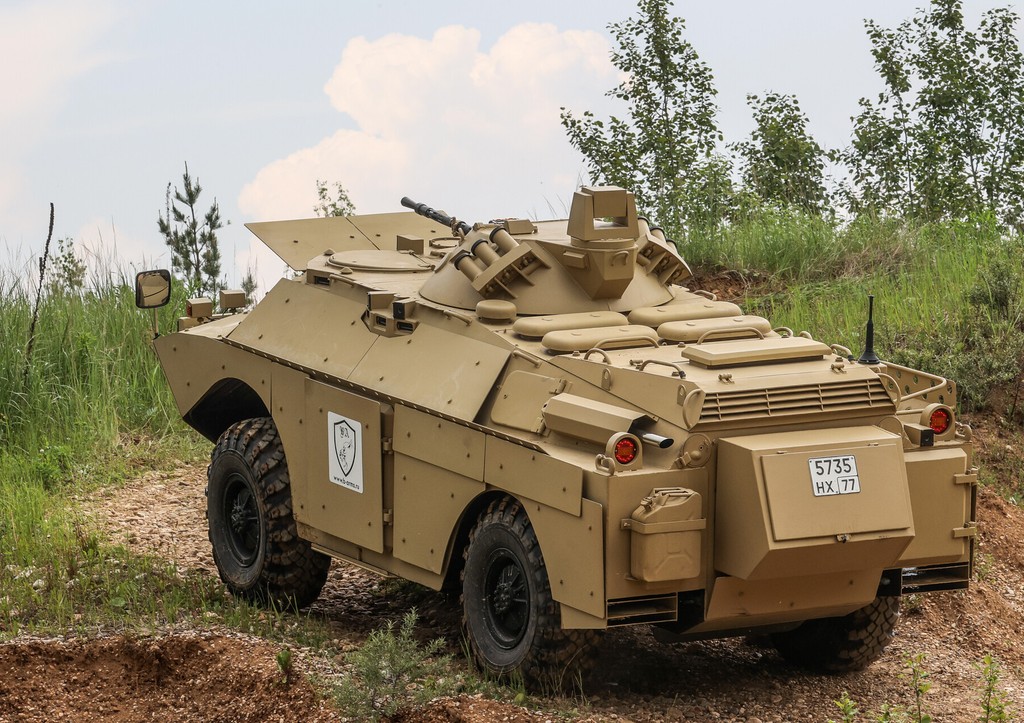

The BRDM-2, a product of the Soviet military-industrial complex, made its debut in the early 1960s. It was developed as a successor to the earlier BRDM-1 and designed to meet the evolving needs of the military. This 4×4 wheeled amphibious vehicle was primarily conceived to fulfill the roles of reconnaissance, patrol, and surveillance in various terrain types, including hostile environments. Its versatile nature made it well-suited for the military doctrines of the time.
Key Features and Capabilities

The BRDM-2 boasts several remarkable features that contribute to its enduring popularity. Its armored hull, constructed with rolled steel, provides protection against small arms fire, artillery shell splinters, and chemical agents. The vehicle can accommodate a crew of four, with a driver, commander, and two scouts. A central feature of the BRDM-2 is its amphibious capability, enabling it to traverse rivers, lakes, and other bodies of water with minimal preparation.
Powered by a V-8 water-cooled engine, the BRDM-2 can achieve a top speed of around 100 kilometers per hour on roads and approximately 10 kilometers per hour when afloat. This combination of speed and versatility allows it to swiftly respond to changing battlefield scenarios.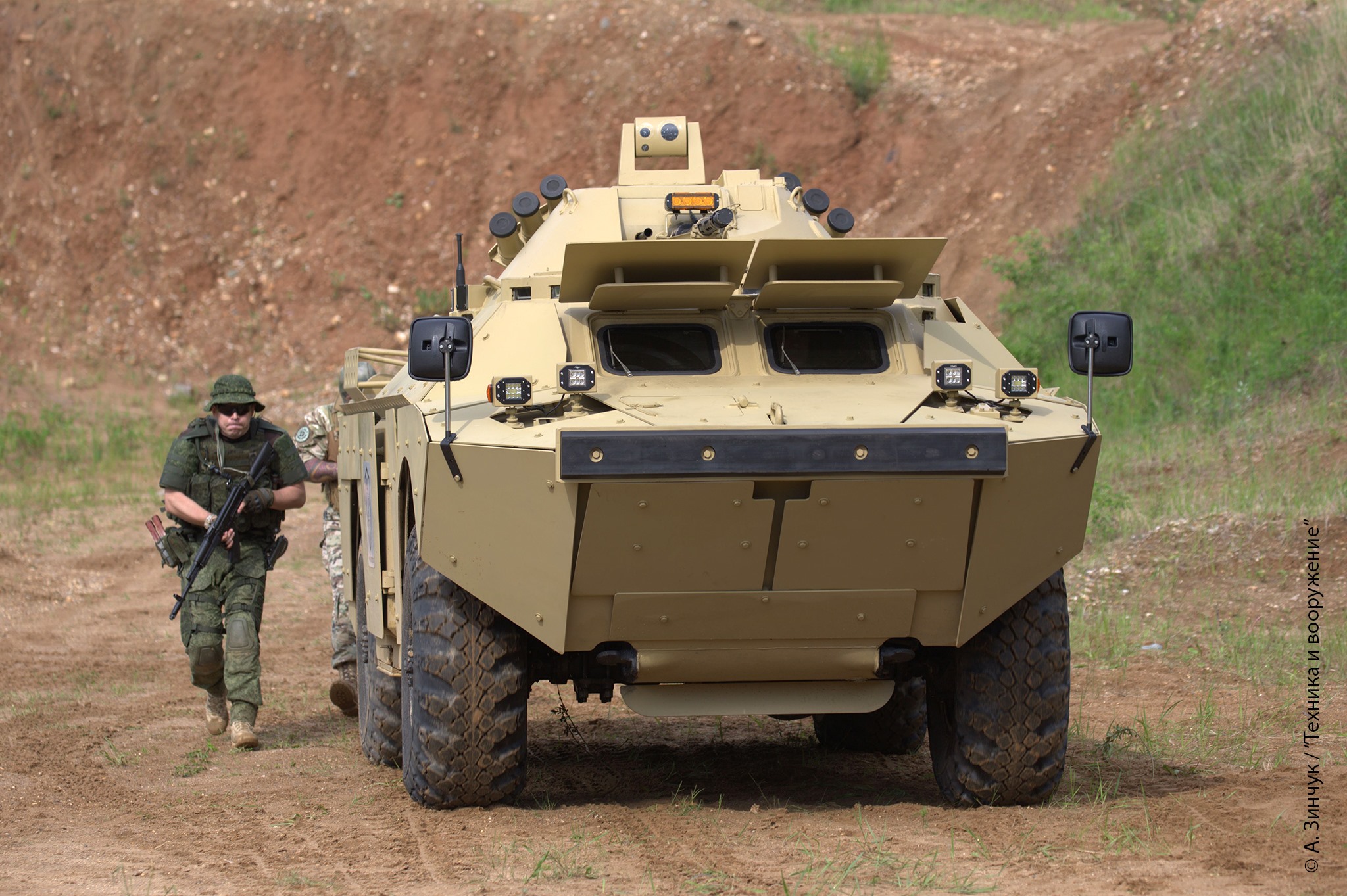
One of the standout features of the BRDM-2 is its armament. It typically comes equipped with a 14.5mm KPVT heavy machine gun and a coaxial 7.62mm PKT machine gun, providing formidable firepower. Additionally, it can be fitted with various anti-tank guided missile systems, making it a potent adversary in both reconnaissance and combat roles.
Operational Significance
The BRDM-2 has seen service in numerous conflicts and military operations since its introduction. Its ability to swiftly and effectively scout enemy positions, conduct patrols, and perform security missions has made it a valued ᴀsset in both offensive and defensive roles. The vehicle’s amphibious capability has proven invaluable in crossing water obstacles, often a crucial tactical element in military operations.
The global adoption of the BRDM-2 speaks to its reliability and adaptability. Various nations, including former Warsaw Pact countries and former Soviet republics, continue to use it in their armed forces. It has also been employed in a peacekeeping role by several United Nations missions. The vehicle’s longevity in service is a testament to its enduring design and functionality.
Modernization and Variants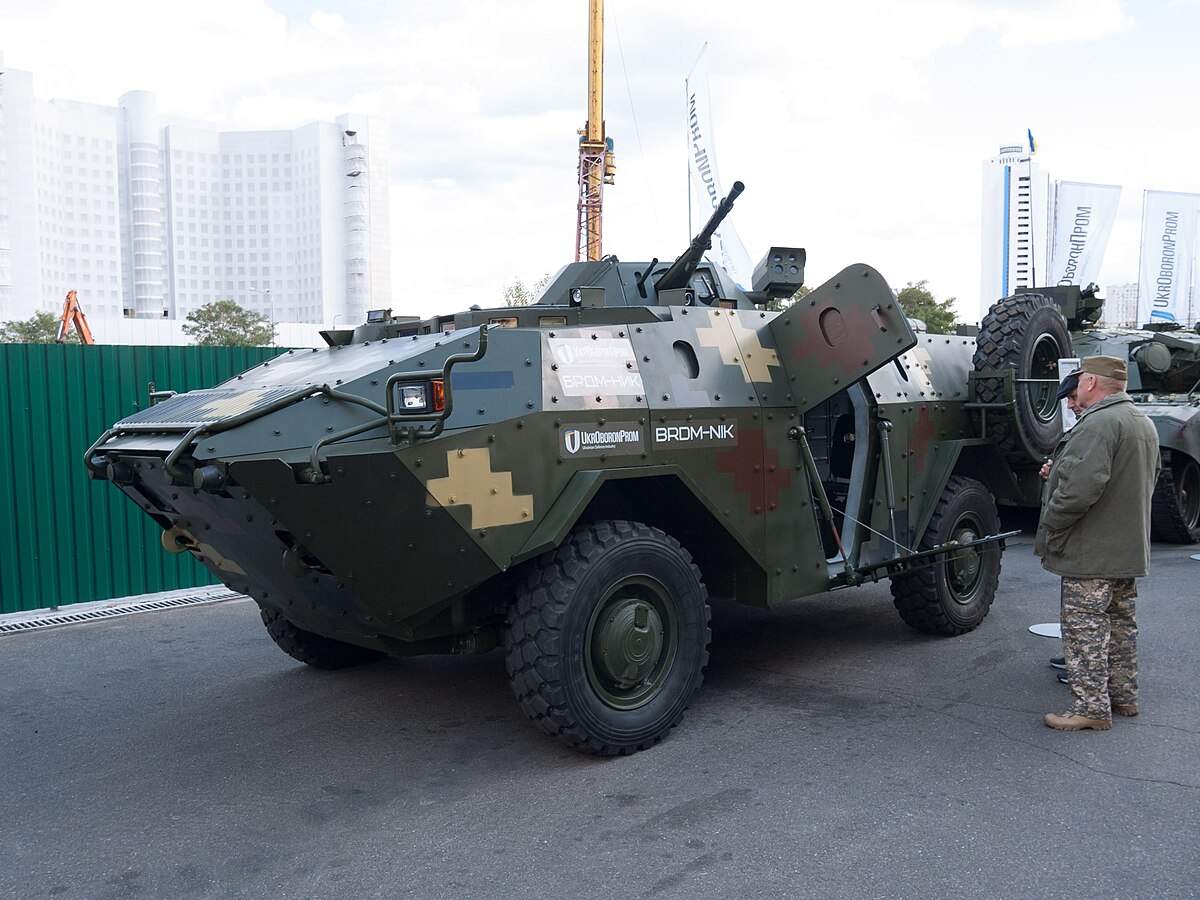
Over the years, the BRDM-2 has seen various upgrades and modifications to enhance its performance and extend its service life. These improvements include enhanced engine power, better armor protection, improved communication systems, and the integration of more advanced weapon systems. Additionally, different variants of the BRDM-2 have been developed for specific roles, such as command and control, anti-aircraft defense, and chemical reconnaissance.
Conclusion
The BRDM-2, with its enduring service history, impressive capabilities, and adaptability, remains a crucial ᴀsset in modern military operations. Its ability to perform reconnaissance, patrol, and combat roles while traversing varied terrain and water obstacles has solidified its place as a versatile armored scout vehicle. As military technology advances, the BRDM-2 continues to evolve, ensuring its relevance in contemporary warfare. Its storied past and ongoing presence in numerous armed forces worldwide attest to the enduring legacy of this remarkable vehicle.