Jan Bartek – AncientPages.com – Archaeologists have used radiocarbon dating to analyze the oldest true wooden frame saddle in East Asia, revealing how advances likely aided the rise of Mongolian steppe cultures in equestrian technology.
A saddle built from a wooden frame is sturdy on horseback, facilitating the addition of stirrups. As such, it is able to carry more weight and provides the rider with greater control, allowing for different kinds of mounted combat.
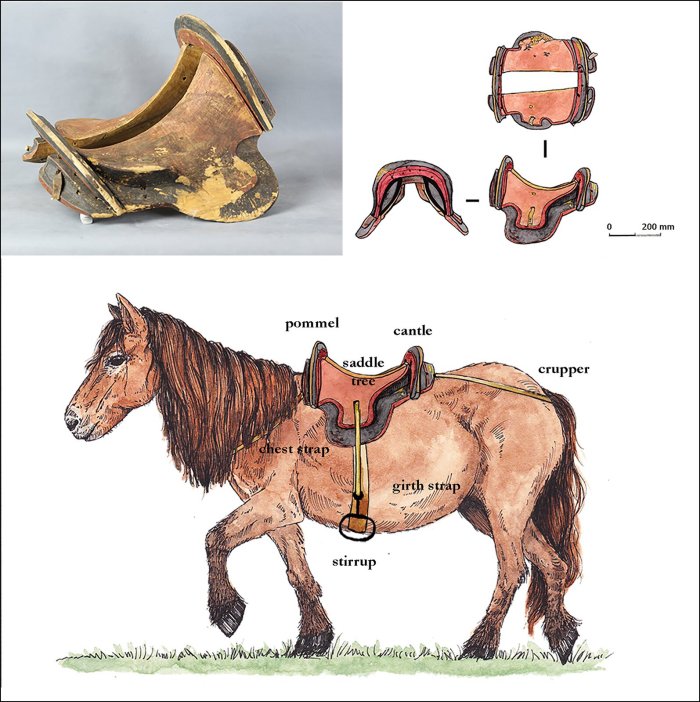
Credit: Antiquity (2023). https://doi.org/10.15184/aqy.2023.172
“Despite their ubiquitous presence within modern equestrian activities, saddles and stirrups were not used during the early centuries of horse-back riding,” state the authors. “Their development revolutionized mounted warfare and contributed to far-ranging social change across Eurasia but the origins of this technology remains poorly understood.”
To trace the beginnings of this revolution, a team of archaeologists from institutions in Asia, Europe and North America studied the saddle, which was found in a human and horse burial at the cave of Urd Ulaan Uneet in western Mongolia. Their results are published in the journal Antiquity.
Calibrated radiocarbon dates place the saddle between AD 267–535, making it the oldest example of a true frame saddle from East Asia.
Additionally, further analysis of the materials that make up the saddle found that they were sourced nearby. The leather is from a domestic horse, which were bred in the area, and the wood from local birch trees.
This suggests that the horse cultures of the eastern Eurasian steppe not only used this new riding technology, but were also instrumental in its development and manufacture. Other finds from Mongolia dating to around the same time period include early metal stirrups.
Importantly, the period to which the saddle dates corresponds to the rise of the Rouran Khaganate, a powerful Proto-Mongolic “imperial confederation” that conquered much of Inner Asia. New saddle technology that facilitated mounted combat likely aided this success.
The Khaganate took control of Inner Asia through military victories, so its rise may not have been possible without this advanced saddle technology. As such, this particular find could have dramatic implications for our understanding of East and Central Asian history.
See also: More Archaeology News
“These new improvements to equestrian combat may have contributed to the formation of early steppe polities,” state the authors. “Our findings raise the compelling possibility that the rise of the Rouran was aided by technological supremacy linked to the early use of frame saddles and metal stirrups.”
The study was published in the journal Antiquity
Written by Jan Bartek – AncientPages.com Staff Writer





